Melanoma is a rather aggressive and serious type of skin cancer that develops in the melanin-producing cells (melanocytes) of the skin. Melanin is the pigment that is responsible for giving the skin color.
Apart from that, melanoma cancer can also form in the eyes and even inside the throat and nose in some rare cases.
When assessing melanoma causes, experts still aren’t sure what triggers the disease. However, the UV radiation from tanning beds and sunlight can increase the risk of development.
Since May is Melanoma and Skin Cancer Awareness month, it’s only natural that we discuss various skin cancer symptoms, and possible treatment options and talk about preventive strategies and inform you about options when it comes to Melanoma and Skin Cancer Management.
This cancer type has been increasing in people who are under 40 in recent years. By knowing the most obvious melanoma symptoms, patients can get help before the disease spreads, also upping the chances of successful treatment outcomes.
Melanoma Symptoms
Melanoma cancer can develop in any place on the body, but most often, it will form in areas that get sufficient sun exposure. These areas can be the legs, back, arms, and face.
On the other hand, the skin cancer symptoms of melanoma may also show in areas that rarely receive enough sunlight. These are areas like the palms of your hands, soles of your feet, and even fingernail bends.
Early-stage melanoma symptoms often include:
- An existing mole on the body starts to change
- New, unusual-looking, often pigmented growths appear on the skin.
However, you should know that early-stage melanoma won’t always form as a mole – it can also appear in normal skin.
Inspecting Moles
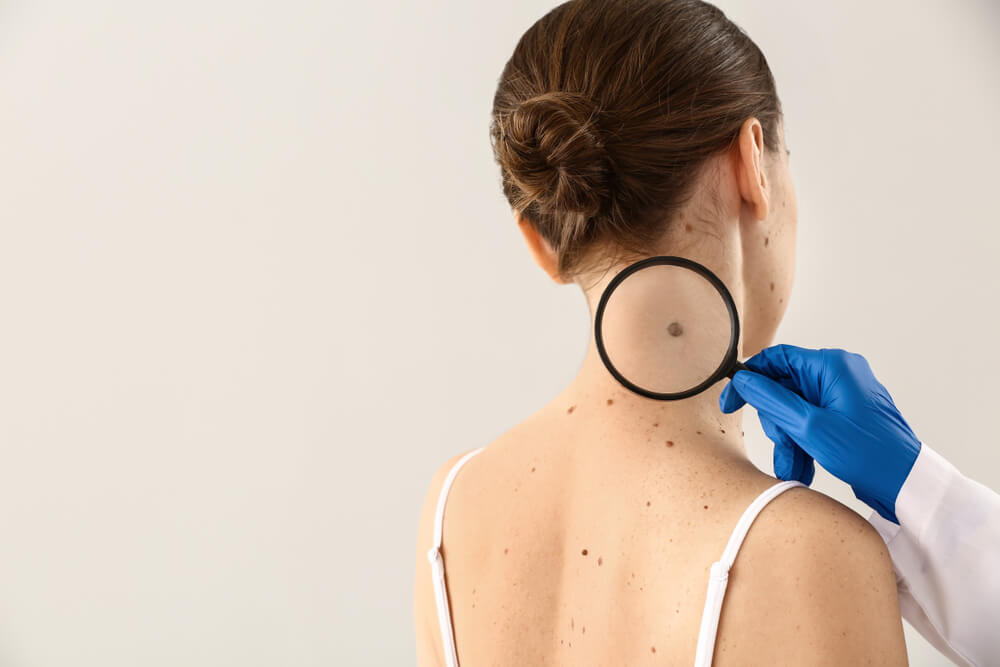
We’ve all seen moles – They are more or less the same color (tan, sometimes black, or brown), and they have a clearly visible border that separates them from the rest of the skin. Generally, normal moles are round or oval, not measuring more than ¼ inches in diameter.
In most cases, these growths appear in childhood, and more may form until people reach 40. By adulthood, most people will have somewhere between ten to 40 of them. Some may change over time, while other moles may even disappear as time goes by.
Moles That May Point To Melanoma Cancer
Unusual moles can be unsettling, but they don’t always point to skin cancer symptoms immediately.
To help people identify potential Melanoma symptoms, they can assess the characteristics of the suspicious mole with the help of five letters: A, B, C, D, and E:
- A – This stands for asymmetrical mole shapes. Look for suspicious moles that have irregular shapes, not being oval or round.
- B – Look for irregular borders. Melanoma symptoms usually manifest in moles that have scalloped or notched borders.
- C – Be vigilant for color changes. Melanoma cancer symptoms include growths with uneven color distributions.
- D – Inspect the mole’s diameter. Be on the lookout for moles that are larger than a quarter inch.
- E – Look whether the mole evolves. Melanoma cancer can show itself as a mole that changes its size, shape, or color. Especially be vigilant when the mole starts to bleed and/or becomes itchy.
When trying to spot early-stage Melanoma, remember that malignant moles can be very different. Some of them may show all the signs we listed above, while others may have only one or two unusual features.
Also, when it comes to catching Melanoma cancer signs early, you should also check out those areas on your body that get little sun exposure. Look for any suspicious changes around your scalp, palms, toes, soles, and even genital area.
These hidden melanomas are rare, but they do develop, especially in people who have darker skin.
As such, hidden melanomas may develop:
- Under the nails: Also called acral-lentiginous melanoma, this is a rare malignancy that may develop under tonsils or fingernails. Sometimes, these melanoma cancers may also develop in the soles of the feet or the palms.
- In the eye: Ocular melanoma will probably develop in the uveal layer, that’s beneath the sclera or the white of the eye. The disease may trigger vision changes.
- In the mouth, urinary tract, digestive tract, or vagina: Mucosal melanoma forms in places where the mucous membrane is present, like in the mouth, nose, anus, esophagus, vagina, and urinary tract. These cancers are even more difficult to spot, as they can often be mistaken for other, more common medical issues.
Melanoma Causes
The malignancy happens when abnormal melanocytes start to grow out of control and develop a cancerous mass.
Still, how these abnormalities start to form is unclear. Experts suggest that a combination of different genetic and environmental causes leads to the development of melanoma cancer. There are medical experts who believe that UV radiation from sun exposure and tanning beds is the leading trigger for malignancy. Even then, UV exposure isn’t responsible for all melanomas (especially hidden ones). This may indicate that other factors are more prevalent in the development of this type of skin cancer.
Melanoma Cancer Risk Factors
So far, here are the factors that may increase the risk of developing the disease:
- A history of severe sunburns: Blistering sunburns can increase the odds of developing melanoma.
- Having fair skin: less melanin means less UV radiation protection. People with light eye colors, red or blond hair and freckles are at a higher risk of developing the disease than people with darker skin complexions. Still, this doesn’t mean that those with darker skin don’t have to be careful.
- Too much ultraviolet light exposure: Not using sunscreen when outside and too much tanning bed use may lead to the development of different skin cancer types, not just melanoma.
- Living near the equator: People in this area receive higher UV radiation as the sun’s rays are more direct.
- A family history of the disease: When close family members have developed the condition (like a sibling or parent), you may also be prone to it.
- Many and unusual moles on your body: Dysplastic nevi, or a condition when you have larger and irregular moles, can increase the risk of melanoma.
- A weakened immune system: Some medications, conditions, or diseases may impair the immune system, increasing the odds of developing several diseases, including skin cancer.
Melanoma Prevention

While there’s no way to entirely prevent the disease, you can reduce the risks by:
- Avoiding going outside in the middle of the day
- Wearing adequate sunscreen year-round
- Wear protective clothing such as baseball caps, visors, sunglasses, and more
- Check your skin (and moles for irregularities
Once the cancer is diagnosed, doctors will assess the stage of the disease and will lay out the best course of action. Often, surgery is the primary treatment, but experts may also choose to incorporate chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy based on the severity of the disease and the patient’s medical state.
Stay Vigilant for the Warning Signs
Melanoma is an aggressive malignancy that’s often hard to detect early on. By taking the necessary protective precautions and checking your skin regularly, you can greatly reduce the odds of developing the disease yourself.
However, if you need more info on the subject or wish to voice your concerns, feel free to reach out to our practice.

