Ensuring optimal sexual wellness is vital for women, and a key aspect of this is regular STD testing. By emphasizing the importance of STD testing in safeguarding one’s sexual health, addressing various types of infections like HPV, herpes, chlamydia, and gonorrhea becomes imperative. This comprehensive guide will navigate through the recommended frequency for testing, how to access confidential testing services, and, most importantly, work toward destigmatizing the conversation surrounding sexual wellness. Join us to empower your sexual health journey with knowledge, confidence, and care.
The Crucial Role of Regular STD Testing
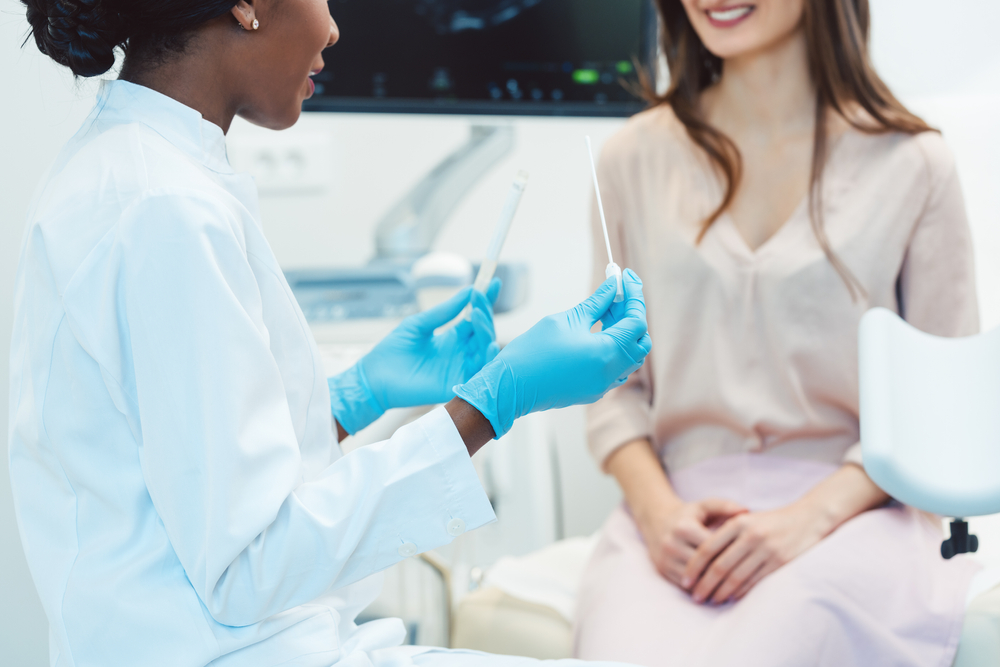
Disclosing the Impact of STDs on Sexual Health
STDs, if left unchecked, can have significant consequences on a woman’s sexual health. They can lead to serious health issues, including chronic pain, infertility, and, in some cases, increase the risk of acquiring other infections such as HIV. HPV, for instance, is known to cause cervical cancer, which is preventable through regular screening and vaccination. Herpes, while not curable, can be managed with medication to reduce and prevent outbreaks, thus minimizing the risk of transmission. Chlamydia and gonorrhea, though often asymptomatic, can cause pelvic inflammatory disease if untreated, potentially leading to infertility.
Regular STD testing is crucial not only for treatment but also for preventing the spread of infections to partners. By recognizing the impact of STDs on sexual health, women can take control of their well-being through proactive measures and responsible sexual practices.
The ABCs of STDs: Knowing What You Could Encounter
Understanding the spectrum of STDs is the first step toward prevention and management. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection, often clearing on its own but sometimes leading to genital warts or cervical cancer. Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) presents as painful sores and can be passed even without visible symptoms. Chlamydia and gonorrhea are bacterial infections that are especially concerning due to their potential to cause serious reproductive issues if not treated early. These STDs can be asymptomatic, which means regular testing is vital for early detection and treatment. Less common but equally important to be aware of are infections like syphilis, trichomoniasis, and HIV, each with its own set of symptoms and health implications. Knowledge of these infections and their effects is a powerful tool for any woman prioritizing her sexual health.
Identifying the Right Time and Frequency for STD Testing
The timing and frequency of STD testing hinge on several factors, including age, sexual activity, and overall health. Generally, sexually active women under 25 should be tested for gonorrhea and chlamydia annually, as they are at a higher risk for these infections. Women over 25 with multiple partners or a partner with an STD should also get tested yearly.
For those in monogamous relationships, the frequency may be less; however, regular screenings are still important. HPV testing should begin at age 30, typically done alongside a Pap test every three to five years. Herpes testing is advised if you or your partner have symptoms or if you’ve had contact with someone who has herpes. It’s essential to discuss your sexual history with your healthcare provider to determine a testing schedule tailored to your specific needs and to ensure early detection and peace of mind.
Normalizing Conversations on Sexual Health and STDs
Breaking the silence on sexual health and STDs is vital for creating a culture that prioritizes wellness and prevention. Open conversations about sexual health can lead to better understanding and less fear around STD testing. Women should feel empowered to discuss their sexual health with partners, peers, and healthcare providers without shame or embarrassment. By normalizing these discussions, we can dismantle stigmas and encourage individuals to seek information and testing. Healthcare providers play a key role in this process by creating a welcoming environment where women can ask questions and express concerns.
Educational resources and community support also contribute to a more informed public, where the spread of STDs can be reduced through collective awareness and action. When conversations about sexual health become as routine as those about other aspects of health, we take a significant step towards a healthier society.
Understanding STD Prevention
Efficient STD Prevention: First Step Towards Sexual Wellness
Preventing STDs is a foundational aspect of maintaining sexual wellness. Effective prevention starts with education about safe sex practices, such as the consistent use of condoms and dental dams during intercourse. Vaccinations, like the HPV vaccine, offer protection against certain types of viruses and are a proactive measure in STD prevention.
Regular communication with partners about sexual history and health is also crucial, as it promotes transparency and informed decisions. Additionally, reducing the number of sexual partners and avoiding sexual contact with those known to have an STD can significantly decrease the risk of transmission. Abstinence is the only surefire way to prevent STDs, but for sexually active individuals, combining education with protective measures is the most efficient way to ensure sexual wellness and health.
Decoding STDs: Herpes, HPV, Chlamydia, and Gonorrhea
Understanding the specifics of prevalent STDs such as herpes, HPV, chlamydia, and gonorrhea is crucial for effective prevention. Herpes, characterized by sores and blisters, can be managed with medication but not cured. Using condoms can reduce the risk of transmission but not eliminate it, as the virus can affect areas not covered by a condom. HPV is widespread, and certain strains can lead to cancer, making vaccination an important preventative measure.
Chlamydia and gonorrhea are bacterial infections that can be cured with antibiotics, yet they often go unnoticed due to their subtle or nonexistent symptoms. Regular screening is essential for early detection and treatment to avoid complications. Knowing the transmission methods, symptoms, and prevention strategies for these STDs empowers women to take proactive steps in protecting their sexual health and preventing the spread of these infections.
Confidential Testing: Ensuring Your Privacy
Confidential testing is a cornerstone of STD prevention and care. Privacy concerns are a significant barrier to seeking STD testing for many women. Therefore, healthcare providers are committed to ensuring that your personal health information remains secure. When you undergo STD testing, your results are handled with the highest level of confidentiality as mandated by privacy laws like HIPAA. Clinics and labs are required to maintain strict protocols so your health data is protected. Furthermore, anonymous testing options are available for those seeking an extra layer of privacy. By choosing confidential testing services, you can feel secure in knowing that your sexual health information is private, which should encourage more women to get tested regularly. This commitment to privacy not only respects your rights but also fosters a trusting relationship between patient and healthcare provider.
Comprehensive Guide to STD Testing
Setting the Picture Straight: STD Testing Process
The STD testing process is straightforward but varies depending on the infection being tested for. Typically, it involves a visit to a healthcare provider where you’ll have a discussion about your sexual history and any symptoms you’re experiencing. Depending on the STD, a blood sample, urine sample, swabs, or a physical examination may be required. For instance, a blood test can detect HIV, syphilis, and herpes, while urine tests or swabs are commonly used for chlamydia and gonorrhea. The HPV test is usually conducted alongside a Pap smear for women. Results can take anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks. No matter the method, the aim is to provide accurate and timely information so that, if necessary, you can start treatment as soon as possible. Remember, early detection is key to managing and treating STDs effectively.
Dispel Your Fears: What to Expect During STD Tests
Approaching STD testing with knowledge can help dispel any fears or anxieties. During a typical STD test, you can expect a healthcare provider first to take a detailed sexual history to determine which tests are appropriate. For a blood test, a small amount of blood will be drawn from your arm. A urine test simply involves urinating into a cup. For swab tests, a healthcare professional may take samples from your genitals, throat, or rectum. For women, a pelvic exam may be necessary to collect samples from the cervix. Discomfort during these procedures is generally minimal and over quickly. Most importantly, you have the right to ask questions at any point. Providers are there to make you feel comfortable and ensure you understand the process. The goal is to keep you informed and at ease throughout the testing.
Confidential Testing Services and Their Working Hours
Choosing a confidential testing service is important for your peace of mind. These services keep your identity and results private. When selecting a facility, consider their working hours to ensure they fit your schedule. Many clinics offer STD testing during regular business hours, while some may provide evening or weekend hours to accommodate those with busier schedules.
Additionally, certain clinics may offer walk-in services, allowing you to get tested without an appointment. It’s essential to check with the specific provider for their hours of operation, as these can vary widely. Some services may also offer home testing kits, giving you the option to test in privacy. Regardless of the hours or methods they offer, rest assured that your results will remain confidential and will only be shared with you unless you give explicit consent otherwise.
Sexual Health Education
Making Sense of Sexual Health Education
Sexual health education is a critical aspect of overall well-being. It provides the knowledge and skills necessary to make informed decisions about sexual activity. Good sexual health education covers a range of topics, from anatomy and reproduction to contraception, STD prevention, and consent. It’s not just about preventing negative outcomes like STDs or unintended pregnancies; it’s also about promoting positive sexual health and relationships. Comprehensive sexual health education empowers individuals to understand their bodies, develop healthy relationships, and respect the choices of others. It should start early and be age-appropriate, continuing through a person’s life. For adults, education can take place in healthcare settings, community centers, or through online resources, ensuring that everyone has access to the information they need to lead healthy sexual lives.
Importance of Sexual Health Education in STD Prevention
Sexual health education is a pivotal tool in STD prevention. It equips individuals with the necessary understanding to recognize the risks associated with unprotected sex and the importance of regular STD testing. Comprehensive education on this topic helps debunk myths and misconceptions about STDs, thereby reducing stigma and fear. It encourages open discussions about sexual wellness, making it more likely for individuals to seek timely medical advice and testing. Knowledge about how STDs are transmitted, the effectiveness of different contraceptive methods, and the signs and symptoms of common STDs are all essential components of prevention. By ensuring that sexual health education is accessible and inclusive, we can cultivate a society that prioritizes health and well-being, ultimately leading to a decrease in the prevalence of STDs.
Coping and Living With STDs

#image_title
Managing Life After an STD Diagnosis
Receiving an STD diagnosis can be a challenging experience, but it’s important to know that many STDs are manageable and treatable. Managing life after a diagnosis starts with education. Learn about your STD, its treatment options, and how to prevent transmission to others. Your healthcare provider will be a key resource in this learning process and in developing a treatment plan. It’s also crucial to communicate with your sexual partner(s) so they can get tested and treated if necessary. Mental and emotional support is equally important. Consider joining support groups or seeking counseling to navigate the emotional aspects of an STD diagnosis. With the right care and support, you can continue to live a healthy and fulfilling life. Remember, an STD diagnosis is not a reflection of your character or worth; it is a health issue that millions of people manage every day.
Confidence After an STD: Inspiring Stories and Support Channels
Living with an STD does not have to limit your life or happiness. Many individuals lead full, healthy lives after a diagnosis, and their stories can inspire others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences through stories helps to humanize STDs, showing that they are common and manageable. These narratives can be found in support groups, online forums, and through healthcare providers. Such platforms provide not only inspiration but also practical advice and emotional support. They can also offer tips on managing symptoms, disclosing an STD to partners, and maintaining a positive self-image. Engaging with these support channels reinforces that an STD diagnosis is a manageable health issue, not a personal failing, and that there is strength in community and openness. Through shared experiences, individuals can regain confidence and continue to build meaningful connections and relationships.



