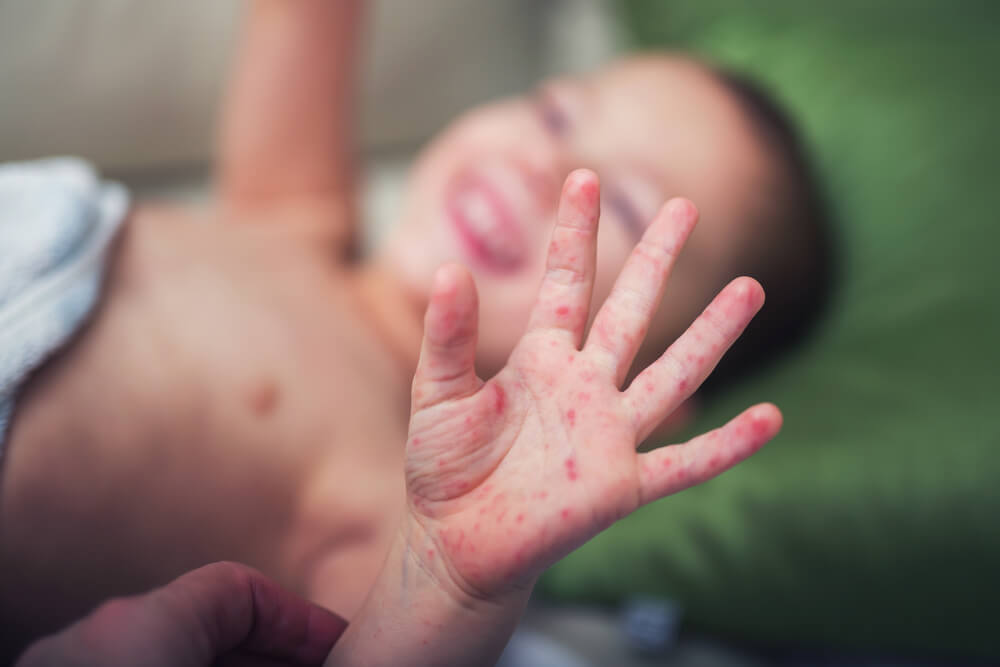
As a parent, you might have heard about a common childhood illness known as hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). This contagious infection typically affects children and can be a cause for concern, which is why proper pediatric care in Miami, Florida, is crucial. Understanding what hand, foot, and mouth disease is, its symptoms, and how it can be managed is essential for any parent. This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with all the information you need to know about this illness.
Understanding Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
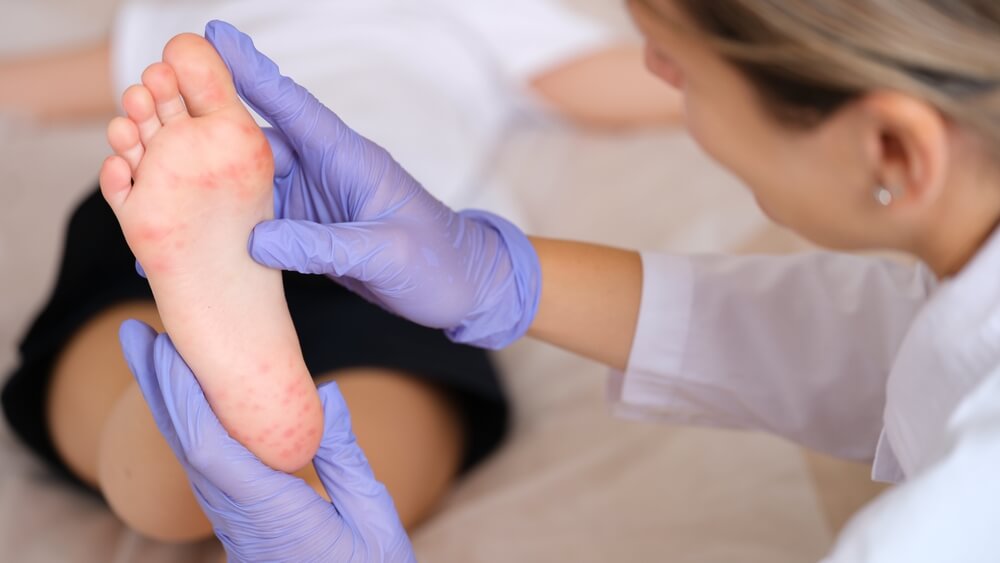
What Is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a viral illness that commonly affects children under the age of 5, but it can also occur in older children and adults. It is caused by a group of viruses, with the Coxsackievirus being the most common. This disease is characterized by sores in the mouth and a rash on the hands and feet, though it can also appear in other areas.
How Does It Spread?
The disease spreads through person-to-person contact, respiratory droplets, and contact with contaminated objects. It’s particularly common in childcare settings due to the close contact among young children.
Recognizing Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Symptoms
Common Symptoms
The primary hand, foot, and mouth disease symptoms include painful sores in the mouth, a rash or blisters on the hands, feet, and sometimes the buttocks, fever, sore throat, and a general feeling of being unwell. These symptoms usually develop 3-6 days after exposure to the virus.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While HFM disease is usually mild and resolves on its own, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional if symptoms are severe, such as if your child is dehydrated or in a lot of pain.
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease in Children
The Impact on Children
Hand, foot, and mouth disease in children can be unsettling due to the discomfort it causes. Younger children may become irritable and have difficulty eating or drinking due to mouth sores.
Preventative Measures
To prevent the spread of hand, foot, and mouth disease in children, encourage regular hand washing, avoid close contact with infected individuals, and disinfect common areas and toys.
Managing Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Home Care Strategies
There is no specific treatment for HFM disease, but symptoms can be managed at home. Offer plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration, soft foods to ease discomfort from mouth sores, and over-the-counter pain relievers, as advised by a healthcare provider.
When to Isolate
Children with hand, foot, and mouth disease should stay home from school or daycare until their fever has resolved and mouth sores have healed to reduce the risk of spreading the virus.
Complications of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
While most cases of hand, foot, and mouth disease are mild, complications can occur. These may include viral meningitis, encephalitis, or a more severe form of the disease caused by different strains of the virus.
Long-Term Outlook
The long-term outlook for children who have had hand, foot, and mouth disease is generally good. Immunity to the specific strain they were infected with is usually developed, but it’s possible to get the disease again from a different strain.
The Role of Vaccination and Research
Emerging Vaccines
While there is currently no widely available vaccine for hand, foot, and mouth disease, research is ongoing. In some countries, vaccines have been developed against certain strains of the virus, showing the potential for broader use in the future. Staying updated on these developments is important, as vaccination could significantly reduce the incidence of the disease.
Research Advancements
Advancements in understanding the viruses causing hand, foot, and mouth disease have led to better diagnostic tools and potential treatments. Research continues to focus on understanding the virus’s behavior, which could lead to more effective ways to combat its spread.
Nutritional Aspects in Management
Importance of Nutrition
Nutrition plays a crucial role in managing hand, foot, and mouth disease, especially in children. Since mouth sores can make eating painful, providing a diet of soft, bland foods and cold treats like ice cream or yogurt can help maintain nutrition while reducing discomfort.
Hydration Is Key
Keeping children well-hydrated is crucial, especially if they have a fever. Offer plenty of fluids like water, milk, or electrolyte solutions. Avoid acidic or spicy foods and drinks, as these can irritate mouth sores.
Psychological Impact on Children and Families
Emotional Support
Hand, foot, and mouth disease, while physically uncomfortable, can also be emotionally taxing for both children and their parents. Children may feel isolated or scared due to the symptoms. Providing emotional support and reassurance is as important as managing physical symptoms.
Supporting Families
Families dealing with hand, foot, and mouth disease can feel stressed, especially if they have to miss work or alter their routines significantly. Communities and healthcare providers should offer support and understanding to these families, helping them navigate through this challenging period.
The Importance of Public Awareness
Educating the Public
Raising public awareness about hand, foot, and mouth disease is crucial. Education can help in early detection, effective management, and prevention of the spread. This includes understanding the symptoms, modes of transmission, and when to seek medical care.
Community Health Initiatives
Health departments and community organizations can play a significant role in disseminating information about hand, foot, and mouth disease, especially in areas with high population density, like Miami, Florida. Organizing community health talks, distributing educational materials, and using social media for awareness campaigns are effective strategies.
Global Perspective on Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
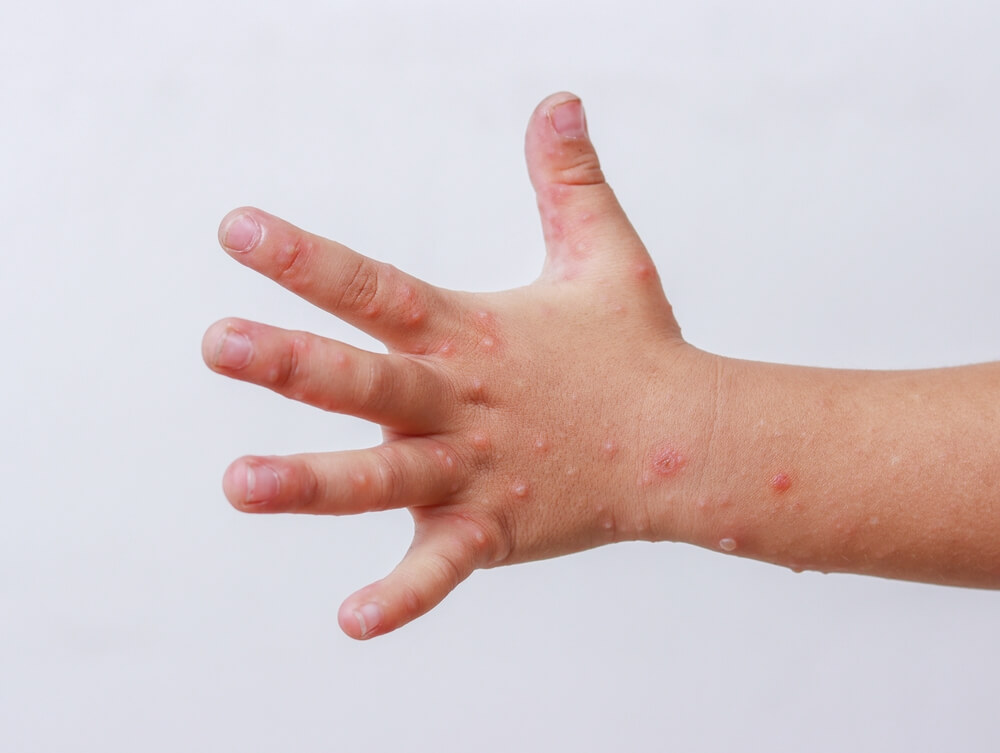
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Worldwide
The incidence of hand, foot, and mouth disease varies globally. In some Asian countries, outbreaks are more common and can be more severe. Understanding the global trends and research in managing this disease can offer valuable insights and strategies for local handling and preventive measures.
Learning from International Experiences
Countries experiencing frequent outbreaks often develop robust strategies to manage hand, foot, and mouth disease. By observing and learning from these international experiences, healthcare providers in Miami and other cities can enhance their preparedness and response to potential outbreaks.
Conclusion: The Role of Healthcare Providers
Dealing with hand, foot, and mouth disease can be challenging for parents. It’s important to stay informed and consult with healthcare providers for the best care. In Miami, pediatric care specialists like Doctor Ana are instrumental in guiding parents through the process of managing and understanding hand, foot, and mouth disease in children. Remember, with proper care and precaution, the impact of this illness can be minimized, ensuring the health and well-being of your little ones.




