What Is a High-Risk Pregnancy?
Most certainly, all pregnancies carry a certain amount of risk. Still, high-risk pregnancies are usually used to describe those cases that cause even more health risks for either the fetus, mother, or both. A high-risk pregnancy may need increased care before giving birth, but during and after as well, to reduce any complication possibilities.
Still, high-risk pregnancies don’t mean that the woman or the baby will have problems. With high-risk pregnancy care, many women have healthy pregnancies and won’t face any problems during labor and delivery.
As such, in this article, we’ll talk about high-risk pregnancies, discuss the most prominent high-risk pregnancy symptoms, and what experts usually do to ensure both the mother’s and the baby’s safety in these cases.
How Common Are High-Risk Pregnancies?
In the US, around 50,000 people experience high-risk pregnancies each year, with the Afro-American population having a three times higher likelihood of dealing with severe pregnancy-related complications.
High-Risk Pregnancy Symptoms and Causes
When exploring the causes of these cases, usually, experts point out the following factors that may make a pregnancy high-risk:
- Specific lifestyle factors such as alcohol abuse, drug addiction, exposure to certain toxins, and smoking.
- Pregnancy-related health conditions
- Being under 17 or over 35 while pregnant
- Preexisting health conditions
- Health conditions related to the pregnancy
When looking at the most prevalent medical risk factors, the following preexisting medical conditions may increase the risks for high-risk pregnancy as well. These conditions may include:
- HIV/Aids
- Diabetes
- Fibroids
- COVID-19
- Autoimmune diseases
- Kidney disease
- Hypertension
- Obesity or being underweight
- Depression and other mental health problems
- PCOS or polycystic ovary syndrome
- Thyroid disease
- Blood clotting problems
On the other hand, the pregnancy-related health conditions that may lead to increased pregnancy risks include:
- Gestational diabetes
- Specific genetic conditions or congenital disabilities in the fetus
- Eclampsia and preeclampsia
- Poor fetal growth
- Multiple gestation.
- Previous cases of preterm birth or labor and various compilations in pregnancies.
As hinted above, in the case of first-time pregnancies over the age of 35 are more likely to have high-risk complications during pregnancy. So far, research shows that they are simply more likely to have more pregnancy troubles than younger people, and these may include pregnancy-related conditions like gestational diabetes or even pregnancy loss.
That said, younger expecting mothers under 17 are also at an increased risk as they are:
- More likely to be anemic.
- Less likely to attend prenatal care consultations.
- More likely to undergo premature birth or labor.
- May be unaware of existing STIs or sexually transmitted infections.
High-Risk Pregnancies: Potential Complications
Some cases may be potentially life-threatening both for the fetus and the mother. The most severe complications may include:
- Preterm delivery
- C-section
- Eclampsia and preeclampsia
- Birth defects
- High or low birth weight
- Excessive bleeding while being in labor, during delivery, or after birth.
- Fetal brain development issues
- Stillbirth
- Miscarriage
- Intensive care unit admission for the mother
- Neonatal intensive care unit admission for the infant.
Diagnosing a High-Risk Pregnancy
Receiving timely and comprehensive prenatal care is of utmost importance. It is the most effective means of identifying and addressing the potential risks associated with pregnancy. Make sure to inform your healthcare provider about your medical background and previous pregnancies. If your pregnancy is deemed high-risk, you may require specialized monitoring throughout the gestational period.
The different tests that experts use to monitor the health of the fetus and the mother may include the following:
- Urine and blood testing to check for specific congenital or genetic conditions.
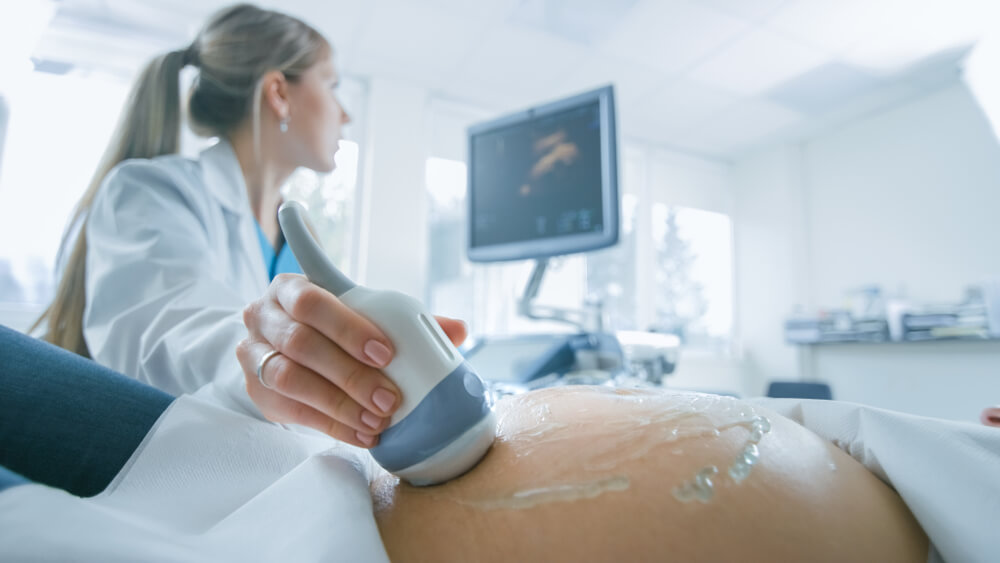
- Biophysical profile to monitor whether the fetus is getting enough oxygen, breathes, and moves, using an ultrasound, and non-stress tests, which monitor fetal heart rate.
- Ultrasonography that creates images of the fetus using sound waves.
Treating and Managing High-risk Pregnancies
Treatment and management for these cases will depend on the specific risk factors. That said, a high-risk pregnancy care plan may include the following:
- Blood pressure monitoring at home
- More frequent obstetrical follow-ups
- Consultation with other medical experts
- Carefully monitoring the medications that the mother uses to manage preexisting medical conditions.
- Closer fetal evaluation and more ultrasounds.
In cases where the mother’s or the baby’s health is in imminent danger, the healthcare provider may even recommend a C-section or labor induction.
Can High-Risk Pregnancies Be Prevented?
Women may be able to reduce the risk of pregnancy-related complications by:
- Avoiding alcohol, tobacco, and drugs
- Identifying potential health problems before actually getting pregnant. Women who are planning to be pregnant should tell everything about their personal and familial medical history.
- Managing preexisting conditions before pregnancy.
- Maintaining a healthy body weight before getting pregnant
- Ensuring that any long-term medical compounds are safe to take while pregnant.
- Planning your pregnancies either over 18 or before you reach 34.
- Practicing safe sex.
Still, it’s vital to understand that many women who are diagnosed with high-risk pregnancies ultimately experience no major problems and deliver healthy infants. And while that’s good news, the same women may be at a slightly higher risk for other health issues, such as:
- High blood pressure
- Type 2 diabetes
- Cardiovascular disease
- Stroke
- Postpartum depression
- Complications in future pregnancies
Also, some high-risk pregnancies may increase the infant’s risk for various medical problems, such as:
- Gastrointestinal diseases
- Breathing problems
- Behavioral issues
- Developmental and growth delays
- Mental health problems
- Diabetes and obesity
- Neurological problems
- Dental, hearing, or vision problems
Lastly, Complications related to pregnancy can manifest up to six weeks after the pregnancy has concluded. It’s crucial to be vigilant about your well-being during this period. If you observe any unusual symptoms or changes, promptly inform your healthcare provider.
Opt for Expert Help and Support
A high-risk pregnancy refers to a situation where various factors increase the likelihood of complications during pregnancy. These factors encompass age and specific preexisting health conditions. In the event of a high-risk pregnancy, additional medical attention may be necessary before, during, and after childbirth.
It is crucial to prioritize comprehensive prenatal care and maintain open and regular communication with your healthcare provider to minimize the potential risks associated with pregnancy complications.
On that note, it’s also essential to find the right experts. Compassionate care, experience, and professionalism can go a long way in ensuring that women experience no issues during their pregnancy.
If you are looking for excellent care, feel free to learn more about Women’s Health Partners by scheduling an appointment with us today.