Having an abnormal pap smear can make you feel worried and anxious. If you are unsure what an abnormal pap smear means, you have clicked on the right article. Below, you will find out what abnormal or positive test results mean, the most common causes of abnormal pap smears, what to do after getting the results, and much more.
That being said, visiting a healthcare professional for regular appointments and check-ups is crucial. Keeping up with the doctor’s appointments is even more critical if you are sexually active or if you have recently changed sexual partners. If you are in the area or you are seeking the best professionals, we recommend Gynecology Specialists in Miami.
What is an Abnormal Pap Smear?
What does “pap smear” refer to, and who should get it? In short, an essential part of a pelvic exam is a pap test or a pap smear. The official longer word for it is “Papanicolaou,” and this name is derived from the name of the doctor who studied cervical cell changes.
A professional will typically perform the Pap smear test on women who are at least 21 years old (when patients become sexually active). However, in some cases, the test may be performed on younger women when there are certain health risks, such as a chance of HIV. Currently, the Pap smear test is the sole method that helps analyze the cells on the cervix to find changes that can result in cervical cancer.
It is important to know that abnormal Pap smear results are actually very common, but only a small percentage of abnormal results are concerning. Read on to find out what the different abnormal results are and what they mean.
Patients who may be at risk of an STI or sexually transmitted infection should consult with a healthcare professional at New Age Women’s Health and get a pap smear. By receiving results early, you can begin the treatment sooner.
How Does a Doctor Perform a Pap Smear?
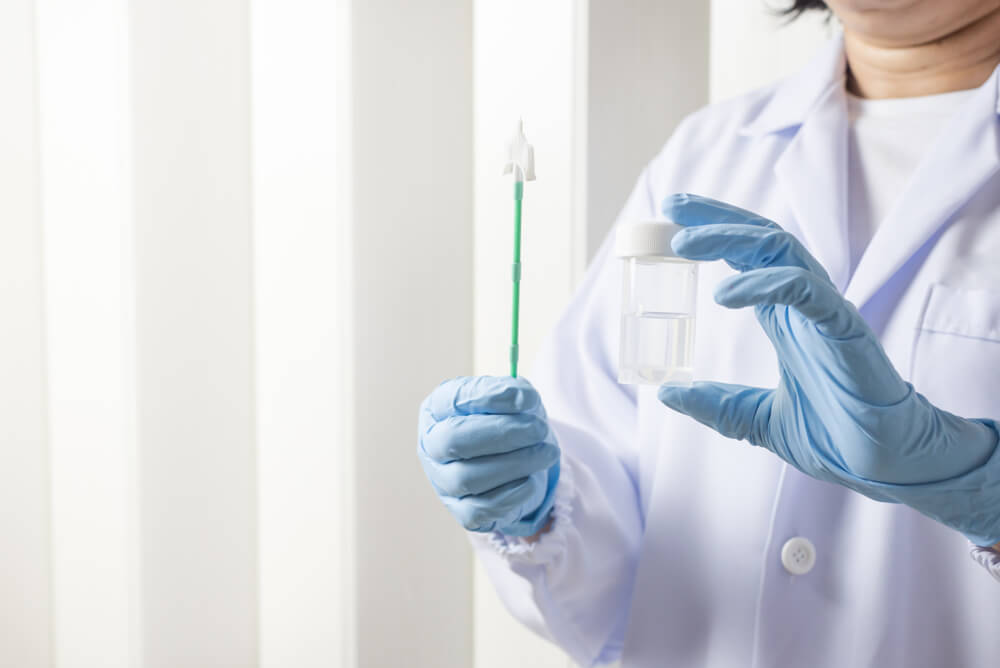

If you have never been to the doctor’s office, you may feel intimidated by the Pap smear test. However, there is nothing to be afraid of. The process is simple and, typically, pain-free. A Pap smear is performed by a healthcare professional, and the entire process is quickly done, often only taking several minutes. The doctor will begin by inserting a speculum into the vagina to check the cervix for abnormalities. The doctor will use a tiny plastic wand with an attached brush to slowly scrape cell samples from the cervix. The sample will be sent to a laboratory for further testing. If you are currently menstruating, it is best to wait until the end of your cycle if it is heavy.
In most cases, patients do not feel any pain. However, some may experience cramping or discomfort when the doctor brushes the cervix. Luckily, the sensation only lasts seconds. The cells will be checked under a microscope for any abnormalities. Finally, the findings will be reported to the doctor.
The Common Results of Pap Smears
Usually, the Pap smear test results come back normal. Nevertheless, sometimes the results may be abnormal. By finding out the abnormality type, your doctor will help you with further treatment. If there are minor cell changes, you may not need treatment. However, moderate and severe cell changes may signify something more serious. These can be pre-cancerous cells, and they can result in cervical cancer.
Here are some of the terms professionals use to define different Pap smear results:
- Normal Results: These results show that you have a healthy cervix.
- Unsatisfactory Results: These test results show that the sample of cells could not be read by the lab technician (as in, not enough cells were collected). Your doctor will reschedule your Pap smear test to take another cell sample.
- ASCUS: This result stands for Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance. While this sounds concerning, it is actually an “in-between” result in which the cells are not completely normal and not completely abnormal. When this result occurs, testing for HPV is typically performed in addition unless you are under 24 years old. An ASCUS result is not concerning if HPV testing is negative. If HPV testing is positive, further testing is usually recommended.
- LSIL: This result stands for Low-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion, which is a fancy way of saying a low-grade abnormality. Depending on your age, when an LSIL result occurs, HPV testing will be performed. If HPV is negative, recommendations can include repeating a Pap smear in one year or a colposcopy. If HPV testing is positive, a colposcopy is generally recommended.
- HSIL: This result stands for High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion, which is equivalent to a high-grade abnormality. When this is seen, a colposcopy is the next recommended step.
- ASC-H: This result stands for Atypical Squamous Cells – cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions. Patients who receive these results will require a colposcopy.
- AGC: This stands for Atypical Glandular Cells. Unfortunately, this result has an association with possible cancer of the inside of the uterus. This result requires a colposcopy as well as an endometrial biopsy.
- Cancer: While this is rare, cancer can be seen as a Pap smear test result.
As a reminder, abnormal Pap smear results are very common, but not all are of immediate concern. Typically, ASCUS or low-grade (LSIL) results are treated very similarly to normal results. This is because ASCUS and low-grade results have a very low chance of turning into cancer over time.
It is also important to know that just because you have an abnormal Pap smear result once does not mean the abnormality is there forever. Very often, with time alone, mild or low-grade abnormalities go back to normal on their own over several months or years. While follow-up is recommended to make sure these results go back to normal, be reassured that there are often no long-term health consequences.
The most common cause of abnormal Pap smears is HPV, or the Human Papilloma Virus. HPV is technically a sexually transmitted infection or STI. There are many different strains or types of HPV, and luckily only a few can cause cervical cancer. Other types of HPV can cause genital warts. Most often, patients with HPV have no symptoms at all and only know they have it if it is found on a Pap smear test. If you have been diagnosed with HPV, be reassured that this virus does not last in your body forever. Typically, it lasts for several months or maybe one to two years. More likely than not, having the HPV virus will not cause any abnormalities to your cervix.
How Can I Prevent Abnormal Pap Smears?
Currently, the only way to prevent abnormal Pap smears is to prevent HPV. Aside from consistent condom use, the only way to prevent HPV is to get vaccinated. Gardasil 9 is the vaccine currently available to prevent HPV, and it provides protection from nine high-risk HPV strains or types. Gardasil 9 is a series of three vaccines given over 6 months. Recently, Gardasil 9 recommendations changed, and it is not recommended to get vaccinated up until age 45. HPV vaccines are typically given to adolescents as young as 9 years old and are often available at Pediatrician or Gynecologist offices.
What is Next?
If your Pap smear test results are abnormal, you may need to undergo additional tests and receive treatment. While abnormal test results can be concerning, it is best to consult with healthcare professionals at a reliable clinic for further guidance.
FAQ

Do abnormal results mean I have cancer?
No, abnormal test results do not directly indicate that you have cancer. However, depending on the severity of the result and if left untreated, you can develop cancer. Because of this, it is vital to stay on track with regular OB-GYN appointments and stay up to date with routine Pap smear testing.
How often should I visit my OB-GYN?
If you are between 21 or older, it is best to visit a gynecologist each year for regular exams. However, if you are sexually active or you are exposed to sexually transmitted infections, you may need to visit an OB-GYN more frequently.
Book an Appointment Today
Receive the health care that you need (and deserve!) from our team of experts. Give us a call today to start protecting your health and your family’s health.