Pregnancy can be blissful, but sometimes problems can occur, making this experience a stressful journey. One of the common problems women experience is anemia during pregnancy. It’s a condition that affects your quality of life and can interfere with your everyday activities.
Fortunately, it’s also a condition that can easily be handled and controlled with a few lifestyle and diet changes.
If you are interested in learning more about low iron during pregnancy and other forms of anemia and how to control them, professionals from Trogolo Obstetrics and Gynecology in Jacksonville will help you with their best advice, so be sure to continue reading this article.
What Is Anemia?
Anemia is a common condition that affects many people. It occurs when your body doesn’t have enough red blood cells to transport oxygen. Your body cannot function properly if it does not receive enough oxygen from the blood.
Hemoglobin is a vital protein found in red blood cells. This protein helps your red blood cells transport oxygen from your lungs to your body by storing oxygen. Additionally, it aids in transporting carbon dioxide from the body to the lungs.
Your body needs a constant supply of iron and vitamins to generate red blood cells and hemoglobin. Without that steady supply, your body won’t manufacture enough hemoglobin to transport oxygen effectively to every organ.
Anemia in Pregnancy
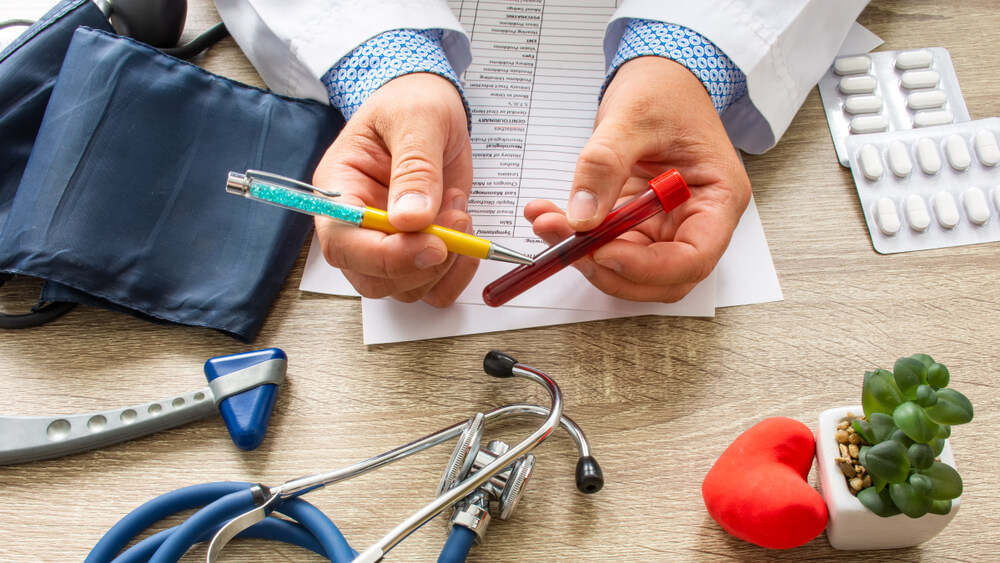

Pregnant women frequently develop anemia because they don’t get enough iron and other micronutrients.
In most cases, low iron during pregnancy will cause slight fatigue during the day and tiredness. However, several severe complications can happen if pregnancy anemia isn’t treated.
For this reason, you must attend every prenatal checkup and let your doctor know if you have any abnormal symptoms.
Types of Anemia in Pregnancy
There is more than one type of pregnancy anemia, and these are the ones:
- Iron-deficiency anemia
- Folate-deficiency anemia (folic acid deficiency)
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
The Causes of Anemia While Pregnant
Mild anemia is typical during pregnancy since blood volume rises. Therefore, your body requires more iron to produce more red blood cells.
Vitamin deficiency can also cause pregnancy anemia, and mostly it’s vitamin C, vitamin B9, and vitamin B12 insufficiency that causes it.
Some women are more likely to suffer from anemia while pregnant if:
- They are pregnant with twins or multiples
- They vomit a lot due to morning sickness
- They have an iron-deficient diet
- Their menstrual flow is really heavy
- They have a history of anemia
Symptoms of Anemia During Pregnancy
You could initially confuse anemia symptoms with typical pregnancy symptoms.
The following symptoms of anemia during pregnancy may appear as the condition worsens:
- Extreme fatigue
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Breathing difficulty
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Decreased body temperature
- Pale skin
- Chest pain
- Irritability
- Problem concentrating
How to Diagnose Anemia in Pregnancy
Anemia can be identified via a blood test called a complete blood count (CBC). This blood test is frequently performed during one of your initial prenatal sessions.
Your healthcare provider will diagnose you with anemia if your red blood cell count is low and may order additional blood tests to determine the specific type of anemia you have.
Severe Anemia While Pregnant
In general, severe cases of pregnancy anemia are not that common. However, you should know that a CBC test result indicating hemoglobin between 6.5 and 7.9 grams per deciliter (g/dL) is considered severe anemia. Your doctor might administer a blood transfusion, most commonly in an outpatient setting, if your test results reveal that you have severe anemia. You can get a sufficient number of red blood cells by a blood transfusion.
Consequences of Untreated Pregnancy Anemia
Anemia that is left untreated may worsen over time. Your organs can suffer damage if your blood oxygen level is too low. Additionally, it makes the heart work harder, raising the risk of arrhythmia and heart failure.
You should be aware that your baby’s growth can be impacted by anemia, particularly in the first trimester. If untreated anemia persists, your kid is more likely to experience developmental issues after birth and be anemic. Anemia also raises the chance of premature delivery and an underweight baby. You should also know you must consume enough iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid to meet the needs of your unborn child.
How to Treat Anemia in Pregnancy
The most common remedy for anemia during pregnancy is taking additional iron. In addition to your prenatal vitamin, your doctor may advise you to take an iron supplement daily or a folic acid one. Take them with a glass of orange juice for the best effects; however, avoid calcium-fortified drinks, as calcium might inhibit iron absorption.
Make sure your diet is high in iron-rich foods like meat, poultry, leafy greens, lentils, and beans, in addition to taking your supplements. The same goes for folic acid and vitamin B12. If your diet is mostly plant-based, you should include a vitamin B12 supplement, as this vitamin is only found in animal products. However, you should talk to your doctor before taking any vitamins and supplements.
Since treatment depends on the underlying cause, discussing your specific requirements with your doctor is crucial. You may need to take folic acid supplements or undergo other therapies if a vitamin shortage or illness causes your anemia.
How to Prevent Low Iron During Pregnancy

Although you can not avoid all occurrences of anemia during pregnancy, getting adequate iron through your food dramatically increases your chances of doing so. That implies ingesting 18 milligrams (mg) of iron daily before becoming pregnant, and your goal should be 27 mg after becoming pregnant.
It would be best to consume a range of healthy foods high in iron while taking prenatal vitamins, which will help meet your needs for other crucial nutrients like folic acid and vitamin B12.
Since food absorbs part of the iron from the skillet when cooked in cast iron, using iron skillets may also increase your daily iron intake.
Final Words
Pregnancy can be stressful, especially for women who will be mothers for the first time. And a condition like this one can cause additional stress. However, you shouldn’t be worried, as it’s somewhat typical and even expected, and you can treat it quickly.
Anemia can be treated and prevented by eating a diet high in iron, vitamin C, and B vitamins. Daily prenatal vitamin use is also helpful. Discuss your risk of this condition with your healthcare provider and any worries you may have.
If you still have doubts about any pregnancy-related topics or don’t have a doctor to guide you through your pregnancy, here at obstetrics in Jacksonville, Florida, you can find help. Our clinic is here to help women on their journey of becoming mothers and help them become and stay healthy.
If you have more questions about women’s health, don’t hesitate to call us today and book your appointment.