Mammary duct ectasia, often referred to simply as duct ectasia, is a frequently misunderstood and usually overlooked condition that primarily afflicts mature women, typically around the time of menopause. Essentially, duct ectasia is the abnormal dilation or widening of the milk ducts in the breast, often leading to an array of uncomfortable and potentially problematic symptoms, including swollen milk glands.
Despite its prevalence, an alarming number of women aren’t aware of the condition, making it all the more important to shed light on this often-neglected healthcare topic. Understanding and addressing conditions like duct ectasia is a priority at Breast Care Center Miami, where we strive to provide comprehensive care and education for women’s breast health.
Considered a benign or non-cancerous condition, duct ectasia’s manifestations might nonetheless be unsettling and distressing for those experiencing it. Disconcerting symptoms such as chronic nipple discharge, which can be clear or colored, and nipple retraction, where the nipple unusually turns inward, are commonly associated with it. It’s due to ductal ectasia symptoms that the condition is often confused with more severe breast conditions, amplifying the need for an accurate understanding of what it is and what it isn’t.
While the causes of mammary duct ectasia remain largely non-conclusive, certain risk factors have been identified. Age is a predominant risk factor, as the condition frequently coincides with menopause. However, it has also been linked to other factors, such as smoking.
Understanding these risk factors could help shine a light on preventative approaches and possible treatment pathways for this condition. Additionally, complications such as mammary gland inflammation may arise, underscoring the importance of early detection and management of duct ectasia.
Detailed Description of Mammary Duct Ectasia
Commencing with an understanding of what is duct ectasia essentially requires a fundamental grasp of the anatomy of the breast. A woman’s breast typically comprises lobules, which are responsible for milk production, and ducts, the passages that lead to the nipple and deliver milk during lactation. Under normal conditions, these ducts are narrow and taut. However, in cases of mammary duct ectasia, these ducts begin to dilate or widen. Over time, the dilated milk ducts can cause the thickening of duct walls, and occasionally, they may become clogged milk ducts, leading to inflammation and swelling, a condition known as ductal inflammation.
While many women with mammary duct ectasia may not experience noticeable symptoms, some individuals commonly report discomfort and abnormal changes in their breasts. Dilated milk ducts and ductal inflammation are generally associated with symptoms such as nipple discharge, which may be clear, white, green, or black. Not to be confused with lactation, chronic nipple discharge is a significant symptom of mammary duct ectasia and is often the first sign that prompts a medical consultation.
Explanation of the Anatomy of the breast and how Mammary Duct Ectasia Occurs
For better clarity, consider the breast as a tree, where the branches represent the ducts and the leaves resemble the lobules. In essence, the primary role of ducts is to act as conduits for milk to travel from lobules to the nipples, much like branches guiding water to the roots. In mammary duct ectasia, the ‘branches’ or ducts become enlarged. This ductal widening can cause the ‘branches’ to thicken and potentially get blocked, thereby leading to inflammation or a more severe condition known as a subareolar abscess if infection sets in.
Often linked with menopause, researchers theorize that the wall-thickening is due to hormonal changes leading the ducts’ muscles to contract, causing the ducts to expand and block.
Moreover, smoking has also been identified as a contributing factor to mammary duct ectasia, accelerating the development of the condition due to its effect on blood vessels supplying the ducts.
Discussion of Common Symptoms and their Significance
The most commonly reported symptoms associated with this ectasia breast condition are:
- Chronic nipple discharge
- Nipple retraction
- Breast inflammation
- Tender or sore breast lump beneath the nipple, occasionally leading to abscesses
While these indications can be a cause of distress, they are usually benign and can be managed effectively with proper medical intervention.
Beyond causing discomfort, these symptoms primarily play an essential role in the early detection and treatment of mammary duct ectasia. Chronic nipple discharge can be the first red flag that facilitates prompt recognition of the condition and timely medical assistance. Similarly, persistent breast inflammation may suggest complications, generally involving infection, and should be promptly addressed.
Overall, greater awareness and recognition of these symptoms are pivotal in ensuring early and effective duct ectasia treatment.
Factors Contributing to the Development of Mammary Duct Ectasia
While the nuances of what exactly triggers the onset of mammary duct ectasia remain elusive, various scientific studies have shed light on several crucial contributing factors. Understanding these contributing factors is pivotal to addressing prevention and optimizing treatment of this ectasia breast condition.
Fundamentally, these factors can be classified into two broad categories:
- Intrinsic influences: age and hormonal changes
- External factors: lifestyle habits and overall health
A Deep Dive into Scientific Studies on Influences such as Age and Hormonal Changes
Age, specifically the phase of menopause, has emerged to be a crucial factor in the development of mammary duct ectasia. Menopause triggers hormonal changes in women, leading to the thinning of the mammary duct lining and the subsequent dilation or widening of the ducts. This process can ultimately result in clogged milk ducts, ushering in symptomatic manifestations of duct ectasia.
Hormonal changes extend beyond just menopause. Endocrine disorders or imbalances may also render certain women more susceptible to developing this breast condition. For instance, estrogen dominance, a condition where a woman has low progesterone compared to estrogen, can predispose breasts to dilated ducts, potentially leading to mammary duct ectasia.
Discussion on the Role of Lifestyle and Overall Health in the Occurrence of Mammary Duct Ectasia
Studies increasingly find correlations between lifestyle, overall health, and the occurrence of breast duct ectasia. In this context, smoking has been found to be one of the most significant lifestyle factors. Nicotine impacts the normal functioning of the delicate blood vessels that maintain the health of the breast ducts, potentially facilitating duct ectasia’s onset. Hence, avoiding smoking could be instrumental in preventing this condition.
Moreover, overall health plays a crucial role in the occurrence and progression of this condition. Maintaining optimal immunity can prevent infections associated with mammary duct ectasia, such as periductal mastitis or subareolar abscesses. In some cases, mastitis treatment may be required if an infection occurs.
Furthermore, individuals with obesity are seen to have a heightened risk of developing duct inflammation, possibly propelling the onset of duct ectasia. Therefore, a well-managed diet, regular physical activity, and a stress-free lifestyle can strengthen overall health, potentially minimizing the risk of developing mammary duct ectasia.
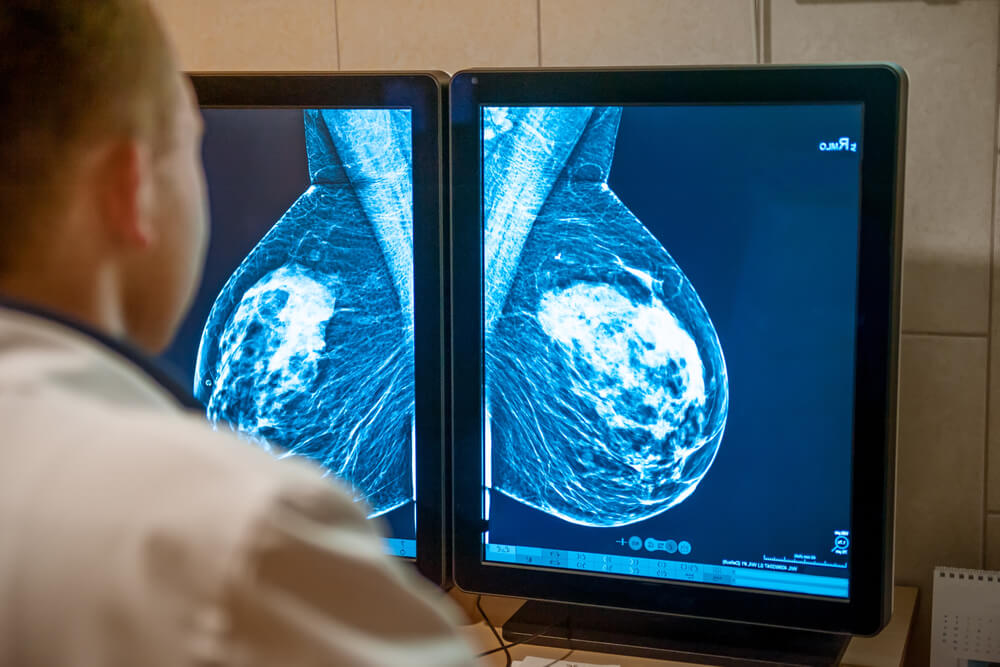
Options for Diagnosis and Treatment
While mammary duct ectasia might be alarming for some due to its symptoms, the methods for an accurate diagnosis followed by effective management and duct ectasia treatment measures are well established within the medical community.
Generally, diagnosis and treatment follow a phased approach, beginning with a general examination, leading to specific testing procedures, and concluding with various treatment options ranging from lifestyle adjustments to surgical interventions.
General Examination and Specific Testing Procedures for Confirming the Diagnosis
When diagnosing duct ectasia, healthcare providers follow a thorough process:
Clinical Breast Examination:
- Initially, healthcare providers conduct a clinical breast examination to check for abnormalities like lumps or nipple discharge.
Additional Diagnostic Procedures:
To rule out conditions like breast cancer, further tests may be recommended:
- Mammography
- Ultrasounds
- Biopsy for closer examination of breast tissue
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques:
- Ductography involves injecting dye into suspected ducts for detailed evaluation.
Examination of Nipple Discharge Samples:
- Nipple discharge samples can be examined in a laboratory to assist in diagnosis.
Collectively, these testing mechanisms ensure the accurate diagnosis of this ectasia breast condition and help rule out any more severe pathologies.
Overview of Treatment Options, from Lifestyle Adjustments to Medical Interventions
Upon diagnosis of mammary duct ectasia, the focus shifts to managing symptoms and ensuring patient comfort. Here’s an overview of treatment options:
Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Lifestyle modifications like quitting smoking, adopting healthier dietary habits, and regular exercise can aid in managing symptoms.
- Good breast hygiene practices and wearing properly fitting bras can also provide relief.
Medical Interventions:
- Medications: Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat ductal inflammation, while analgesics can help control pain.
Surgical Options:
- Surgical interventions may be considered for persistent symptoms or complications such as abscesses.
- Surgical procedures mainly focus on removing the affected duct or ducts.
Regardless of the chosen approach, the goal of duct ectasia treatment is to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and ensure the patient’s overall health and well-being.
Emphasizing Breast Health and Early Detection
The journey of understanding mammary duct ectasia underscores the criticality of early detection and diagnosis in managing any health condition, especially when it pertains to breast health. This ectasia breast condition, with symptoms like chronic nipple discharge, nipple retraction, and, in severe cases, breast abscesses, can potentially disrupt your daily life.
However, it is essential to remember that it is typically non-cancerous and considerably manageable under medical guidance.
Early detection plays a vital role in minimizing complications and ensuring the most effective management of this condition. Knowing the signs, such as unusual nipple discharge, breast discomfort, or visible nipple changes, is the first step towards proactive healthcare.
Subsequently, reaching out to a healthcare professional without delay is paramount. They can meticulously evaluate your symptoms, conduct necessary examinations or diagnostic tests, and provide the most appropriate treatment tailored to your needs.
Further, maintaining regular breast self-examinations or clinical breast exams can help note any changes or abnormalities that might indicate the onset of mammary duct ectasia or any other breast conditions. Particularly for those identified with risk factors such as being of postmenopausal age or smokers, regular checks can serve as a preventive step.
Indeed, the significance of mammary duct ectasia lies in the valuable lesson it provides us – that being proactive about our breast health and ensuring timely medical consultation can effectively manage potential health concerns. It reassures us that with knowledge, diligence, and medical advancements, living healthily and comfortably is entirely within our reach.