The thyroid is a small gland located in the neck, around the trachea. It produces hormones that play an essential role in many bodily systems. The thyroid gland produces vital hormones such as thyroxine (T4) by synthesizing iodine. Thyroxine passes through the bloodstream to the tissues, while a small amount of the hormone gets converted to triiodothyronine (T3).
The brain regulates the thyroid gland’s functions using a feedback mechanism. When the body has a low thyroid level, the brain through the hypothalamus produces a hormone called thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) that stimulates the pituitary gland to release the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). The hypothalamus and the pituitary gland control the thyroid gland, and disorders in these tissues that affect the functioning of the thyroid gland lead to thyroid problems.
There are different types of thyroid problems that either affect its function or structure. Some common thyroid disorders are hypothyroidism which could be congenital or acquired, hyperthyroidism such as Graves disease, Goiter, thyroid cancer, and thyroid nodules. Thyroid disease is a medical condition that causes symptoms due to over- or under-functioning of the thyroid gland. With National Thyroid Awareness Month coming up, it’s important that you know about this condition.
Hypothyroid vs Hyperthyroid
Hypothyroidism is an illness where the thyroid gland fails to generate an adequate amount of thyroid hormone. It can develop from issues within the thyroid gland, hypothalamus, or pituitary gland. Common symptoms of hypothyroidism are dry skin, fatigue, constipation, being cold, poor concentration, depression, fluid retention, and muscle and joint aches.
Babies can be born with a thyroid problem. Most cases of congenital hypothyroidism happen because the thyroid doesn’t form correctly. It is possible that the baby’s thyroid did fully develop, but can’t make normal amounts of thyroid hormone. It is important that we identify if a baby has a thyroid problem because without treatment, children with congenital hypothyroidism can develop permanent mental disabilities. It is important to ask your pediatrician about the results of the newborn screen that is done before a baby is discharged from the hospital.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. It is characterized clinically by gradual thyroid failure with or without goiter formation due to the autoimmune mediated destruction of the thyroid gland. Nearly all patients have high serum concentrations of antibodies against 1 or more thyroid antigens which causes inflammation of the thyroid.
Some other causes of hypothyroidism include thyroid hormone resistance, post surgical, radiation treatment, medications such as lithium or amiodarone among others, iodine deficiency, damage to the pituitary gland, and rare disorders that can infiltrate the thyroid.
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid produces too much hormone. Common symptoms include nervousness, irritability, muscle weakness, shaking, sleeping problems, and sudden weight loss. Women can experience irregular menstrual periods, or their periods can stop altogether. Some conditions that cause hyperthyroidism include Graves’ disease, thyroid nodules, toxic multinodular Goiter, and excessive iodine consumption.
Goiter
Goiter is the condition where the thyroid gland enlarges regardless of the cause. It is not a specific disease, and it’s usually associated with hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, or normal functioning of the thyroid.
Thyroid Nodules
Nodules are abnormal masses or lumps within the thyroid that are usually caused by benign cysts. They vary in size and can be single or multiple. Nodules may cause symptoms associated with compression of nearby organs.
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is more common among older women than men or younger people. About two-thirds of cases affect people under 55 years. There are different types of thyroid cancer, depending on the specific thyroid cell type that is cancerous. When diagnosed early enough, most cases of thyroid cancer are treatable and have high survival rates.
Diagnosing Thyroid Disorders
There are special tests that are normally used to test thyroid disorders. Doctors also go through medical history and perform a physical exam. Blood tests are also done to measure thyroid hormone levels and TSH. In certain cases, they also measure antibodies against the thyroid tissue, such as anti-thyroperoxidase (TPO), anti-thyroglobulin, or TSH receptor-stimulating antibodies.
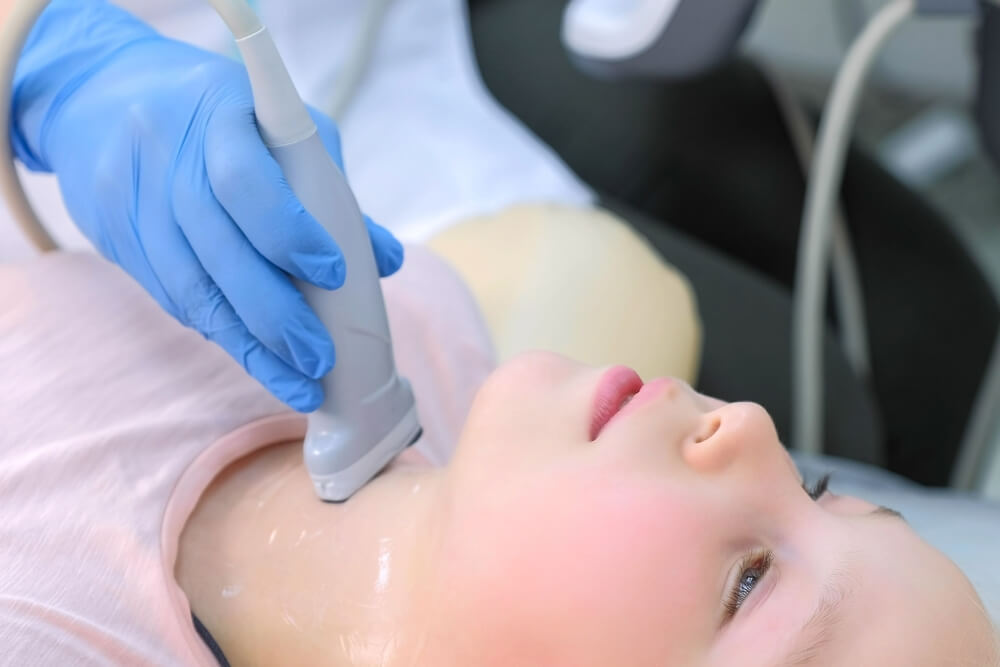
Enlargement in the thyroid gland or thyroid nodules requires imaging tests. Ultrasound is usually used to get a better view on the consistency of the tissue in the gland. Radioactive iodine is often used to perform thyroid scans to access the thyroid nodules’ function. Tissues of the thyroid gland are usually removed using fine needle aspirations and biopsy for examination.
Treating Thyroid Disorders
Surgeries and medications are usually used to treat thyroid disorders. The treatment depends on the specific thyroid disease. Thyroid medications are often administered to replace insufficient thyroid hormone in hypothyroidism or can be given to make it harder for the body to make thyroid hormone in the setting of hyperthyroidism.
In the case of the presence of a goiter and the presence of a hyperfunctioning nodule in the thyroid gland, surgery is performed. It is usually performed when there is a high chance of thyroid cancer. A patient has to take synthetic thyroid when the thyroid gland gets removed in surgery. Graves’ disease can be treated with radioactive iodine or thyroid surgery.
Thyroid Awareness Month
January is Thyroid Awareness Month, and it is usually observed yearly. There are different ways you can observe this day, including getting the thyroid neck check, encouraging friends and family to get tested, or making a donation.
The thyroid neck check is a simple procedure that you can do regularly and not just during January Thyroid Awareness Month. You can use a mirror and a glass of water to check the neck’s lower front area around the thyroid gland. Tip your head back, and then drink the water. Carefully check your neck for any protrusions or bulges as you swallow. If there are any bulges, contact your doctor as you may have a thyroid nodule or an enlarged thyroid gland.
Encouraging a friend or family member to get tested for thyroid issues can help them find treatment quicker. Be on the lookout for symptoms of thyroid disease. About 20 million Americans suffer from a thyroid condition. You also make a donation to the many thyroid research or treatment institutions available.
Importance of Thyroid Disease Awareness Month
National Thyroid Awareness Month helps to emphasize the crucial role of the thyroid gland. When it produces too little or too many hormones, it causes an imbalance in other body systems. The month also encourages people to get tested. It creates awareness of the symptoms to look for and early testing. National Thyroid Awareness Month also promotes early treatment. Early testing leads to early treatment.
Thyroid Cancer Awareness Month
September is Thyroid Cancer Awareness Month, and it’s observed worldwide. It began in 2000 as a week in September and expanded to the whole month in 2003. The month promotes cancer awareness for early detection as well as the increase in research to achieve cures for all thyroid cancer.
Thyroid cancer is rare in children. There are four main types of thyroid cancer: follicular thyroid cancer, papillary thyroid cancer, anaplastic thyroid cancer, and medullary thyroid cancer. Papillary thyroid cancer is the most common thyroid cancer, but it’s treatable when diagnosed early. Anaplastic thyroid cancer is an aggressive and rare type of thyroid cancer that spreads quickly and is hard to treat. Some forms of thyroid cancer can run in families like medullary thyroid cancer.
If your child has experienced thyroid disease symptoms, make sure to call the Pediatric Endocrine and Metabolic Center of Florida. We have a state-of-the-art facility dedicated to treating children and adolescents with metabolic and endocrine conditions. Contact us today so we can schedule an appointment for you and your child.


