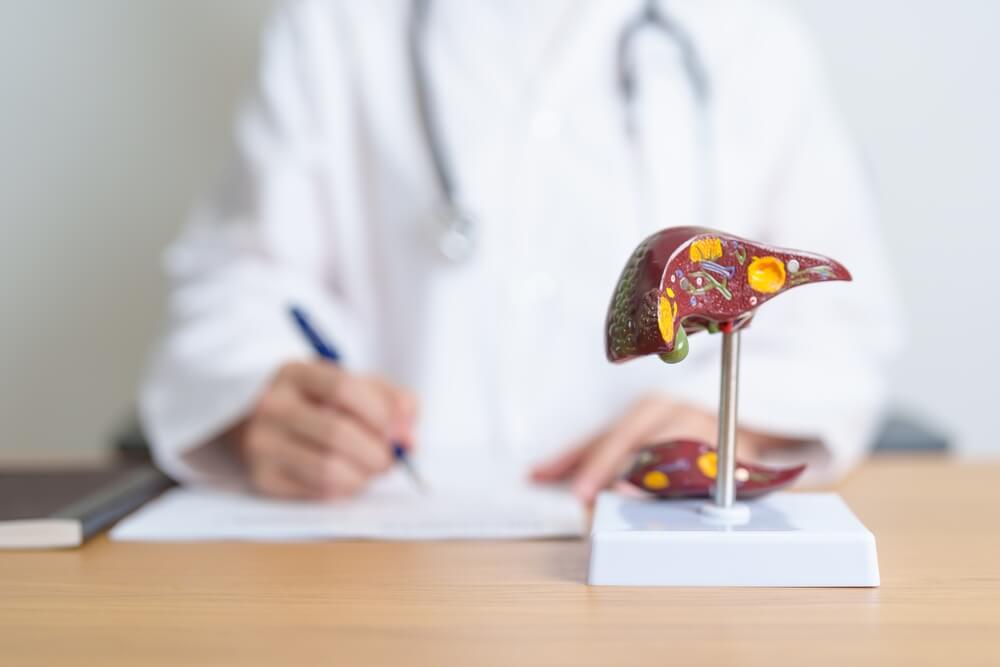
Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy, often abbreviated as AFLP, is a serious but rare pregnancy-related liver disease that can pose severe threats to both the mother’s and baby’s health. This high-risk pregnancy complication typically emerges in the third trimester. A sudden onset of symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, pain in the upper right stomach region, jaundice, and extreme fatigue characterizes it.
The condition, known medically as gestational hepatic dysfunction, occurs due to the accumulation of microvesicular fatty acid within the liver. The precise pathophysiology isn’t entirely understood but is thought to involve mitochondrial dysfunction leading to a disruption in the breakdown of fatty acids, resulting in an overload of fat storage in liver cells – hence the designation ‘fatty liver.’
Statistics indicate that AFLP affects about 1 in every 10,000 to 20,000 pregnancies worldwide. While this might seem relatively uncommon, the gravity of its potential ramifications warrants undivided attention. Maternal liver failure and adverse fetal outcomes, including stillbirth, are possible consequences of untreated or late-treated AFLP, making it a significant health concern during gestation.
For these reasons, it is crucial for expecting mothers and healthcare providers to gain a comprehensive understanding of this pregnancy-induced liver disorder. Familiarity with its warning signs, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment strategies could be instrumental in ensuring a safe and healthy pregnancy and childbirth. If you’re seeking expert obstetric care in Jacksonville, Florida, look no further than Trogolo Obstetrics and Gynecology. Our compassionate team is dedicated to providing exceptional care tailored to your needs.
Causes of AFLP
While the exact cause of acute fatty liver in pregnancy is not entirely known, current research suggests several factors that may contribute to this pregnancy-related liver disease.
Genetics and Pre-existing Conditions
Specific genetic mutations, like those seen in fatty acid oxidation disorders, specifically the long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (LCHAD) deficiency, are associated with an increased risk of AFLP. A woman who carries this genetic mutation or whose partner is a carrier is more susceptible to this liver malfunction during pregnancy.
In addition, pre-existing health conditions such as hypertension, preeclampsia, diabetes, and obesity can potentially exacerbate the risk. However, it is a rarity to develop this condition, even among individuals with the factors above. AFLP seems to be more arbitrary by nature, impacting otherwise healthy mothers and those with high-risk pregnancy complications alike.
Pregnancy-related Factors
AFLP is a disease of the third trimester. Although very rare, it’s been noted on occasions to occur postpartum. This suggests that specific alterations occurring in the mother’s body during this period – the hormonal shifts, physiological stress, and metabolic changes – could have a critical role. However, AFLP also occurs among women in their first or second pregnancy, which removes parity as a significant factor.
One current theory proposes the placenta plays a key role. Precisely, it’s thought that the fetoplacental unit increases the demand for middle-chain and long-chain fatty acid oxidation, which could overwhelm a genetically predisposed mother, leading to AFLP. Yet, much is still left to be understood about this severe pregnancy liver condition, and research is ongoing.

Symptoms and Diagnosis of AFLP
The sudden onslaught of problematic symptoms and the rapid progression of the disease make acute fatty liver pregnancy a significant pregnancy-induced liver disorder among expecting mothers. Understanding the primary symptoms and the medical diagnostic tests is crucial in managing this health concern.
Identifying Symptoms
Identifying AFLP symptoms in expecting mothers is of utmost importance as it’s the first step toward diagnosis. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent nausea and vomiting
- Lack of appetite
- Fatigue
- Discomfort in the upper-right portion of the abdomen
Additionally, the mother may experience:
- Rapid weight gain
- Jaundice
- Symptoms associated with decreased liver function, such as bleeding gums and nose
Less commonly, expectant mothers may also present signs of encephalopathy, including:
- Confusion
- Sleepiness
- In severe cases, coma
Medical Tests for Diagnosis
AFLP is typically diagnosed with a combination of clinical findings and blood tests. Blood tests can reveal raised liver enzymes and bilirubin levels as well as a decreased platelet count, all indicative of a liver threat in pregnancy like AFLP. An ultrasound may also be performed, though its sensitivity can be low for fatty liver disease. The definitive diagnosis of AFLP is often made with a liver biopsy. Still, due to its invasive nature and associated risks, it is usually reserved for when the diagnosis is in doubt.
More recently, non-invasive tests like the FibroScan, which measures liver stiffness, and tests for biomarkers of fibrosis and steatosis in the blood are being used to diagnose AFLP. The place of AFLP diagnosis and treatment in current obstetric practice is still evolving with ongoing research. Regular prenatal care and communication with healthcare providers about unusual symptoms are fundamental in the early detection and management of AFLP.
Treatment and Management of AFLP
The approach to treatment and management of Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy (AFLP) involves immediate comprehensive care and ongoing post-pregnancy monitoring and care. Given that AFLP is a high-risk pregnancy complication, its management is crucial in protecting both maternal and fetal health.
Immediate Care Requirements
Once AFLP is diagnosed, it requires immediate attention due to the risk of serious pregnancy liver conditions and complications like maternal liver failure, bleeding complications, and fetal distress. The cornerstone of treatment is the prompt delivery of the baby, regardless of the gestational age. This alleviates the liver’s strain, allowing it to gradually recover.
Simultaneously, supportive care is essential to manage complications, such as blood clotting disturbances, low blood sugar, or infections. Critical care and monitoring are typically necessary. In some severe cases, expectant mothers might need a liver transplant. However, this is seldom required, considering the liver often recovers once the baby is delivered.
Post-Pregnancy Impact and Care
Despite the immediate resolution of AFLP after delivery, a mother might still feel the impacts of this liver illness in gestation during the postpartum period. The aftermath of AFLP can include depression, post-traumatic stress, and physical recovery challenges such as fatigue and digestive disturbances.
Additionally, it’s crucial for mothers who have experienced AFLP to consider genetic counseling alongside their partners since there may be a risk to future pregnancies. Ongoing research is also important to illuminate the long-term effects of AFLP for mothers and their children. Understanding and monitoring post-pregnancy AFLP impacts are essential aspects of postpartum care to ensure holistic recovery and ongoing maternal health.
Navigating the Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy Journey
In the face of the serious yet rare condition of Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy (AFLP), regular prenatal check-ups and constant communication with healthcare providers are essential. Due to the swift and threatening trajectory of AFLP, timely detection is key to implementing effective treatment strategies and reducing potential maternal and fetal risks. Regular monitoring of general health during pregnancy can also provide early indications of abnormal signs, permitting immediate diagnosis and treatment of this pregnancy-related liver disorder.
Even following childbirth, continued monitoring is paramount in mitigating the postpartum impacts of AFLP. It is also crucial to ensure a holistic and complete recovery for the mother and to diligently track the long-term health of both mother and infant. Sufficient post-pregnancy care, inclusive of both physical and psychological wellness considerations, can play a significant role in facilitating an all-round recovery.
Education and support of women about AFLP and other such high-risk pregnancy complications is an essential tool for increasing awareness and equipping them with the knowledge they need for their health management. Whether they are expectant mothers or women planning a future pregnancy, understanding the symptoms, risks, and treatments related to serious pregnancy conditions like AFLP is an invaluable step toward proactive health management and preventative care. After all, it’s not merely about surviving the journey but thriving beyond it.
For comprehensive obstetric care in Jacksonville, Florida, schedule your appointment at Trogolo Obstetrics and Gynecology today. Take proactive steps towards a safer pregnancy journey. Your well-being is our priority.