Understanding the differences between gestational hypertension and preeclampsia is essential for expectant mothers, their families, and healthcare providers, as these conditions can profoundly affect both pregnancy and overall health. Gestational hypertension vs preeclampsia can often be confused due to their similar presentations, but distinguishing between them is crucial for effective management.
This document aims to clarify what gestational hypertension and preeclampsia entail, outline the symptoms of gestational hypertension, and emphasize the importance of continuous prenatal care for monitoring blood pressure changes.
By becoming informed about these conditions, individuals can more effectively advocate for their health and work closely with specialists, such as those at Trogolo Obstetrics and Gynecology in Jacksonville, Florida, to ensure a safer pregnancy experience.
Understanding Gestational Hypertension
What is Gestational Hypertension?
Gestational hypertension is a condition characterized by high blood pressure that develops after the 20th week of pregnancy in women who previously had normal blood pressure levels. Unlike preeclampsia, gestational hypertension does not involve the presence of excess protein in the urine or other signs of organ dysfunction. This condition requires careful monitoring, as it can potentially progress to preeclampsia if not managed properly.
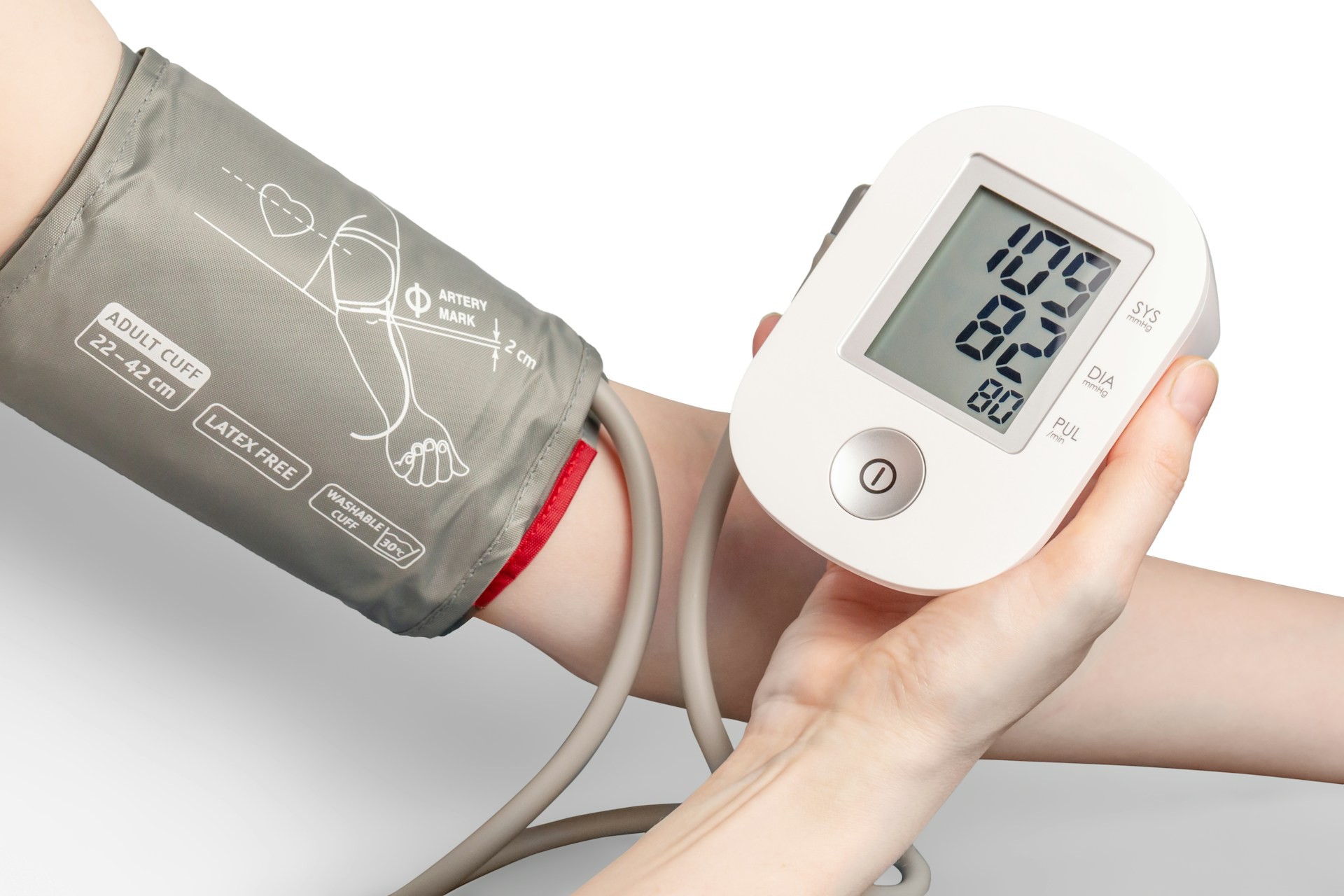
Typically, gestational hypertension is diagnosed when a pregnant woman’s blood pressure readings reach 140/90 mmHg or higher on two separate occasions, at least four hours apart. While the exact cause remains unclear, factors such as a first pregnancy, multiple gestations, and a history of hypertension can increase the risk. Management includes regular prenatal check-ups to monitor the mother and baby’s health, ensuring a safe delivery and reducing the risk of complications.
Symptoms of Gestational Hypertension
Gestational hypertension often presents without noticeable symptoms, which makes regular prenatal check-ups crucial for early detection. However, some women may experience symptoms that warrant prompt medical attention. Common symptoms of gestational hypertension include persistent headaches, visual disturbances such as blurred vision or light sensitivity, and swelling in the hands and face. These symptoms can be mistaken for typical pregnancy discomforts, but they should not be overlooked. If blood pressure reaches severe levels, it can lead to more serious complications, affecting both the mother and the baby’s health.
Monitoring is key; blood pressure checks during prenatal visits help track any changes. If gestational hypertension is suspected, healthcare providers may recommend additional tests to ensure proper management and prevent progression to more severe conditions, such as preeclampsia. Understanding these symptoms empowers pregnant women to advocate for their health and seek timely medical intervention.
Risk Factors and Causes
The exact causes of gestational hypertension remain unclear, but several risk factors have been identified. Women experiencing their first pregnancy are generally more susceptible, as are those expecting multiple babies, like twins or triplets. A family history of hypertension or preeclampsia can also elevate the risk.
Pre-existing conditions, such as chronic high blood pressure, diabetes, or kidney disease, can contribute to the likelihood of developing gestational hypertension. Additionally, lifestyle factors, including obesity and age (particularly women over 35), play significant roles. These factors may affect the body’s ability to regulate blood pressure during pregnancy. While some risk factors, like age and family history, cannot be altered, lifestyle modifications can help mitigate potential risks. Regular prenatal care offers opportunities for monitoring and managing these risk factors effectively, thereby supporting a healthier pregnancy.
Understanding these elements allows women and healthcare providers to work together to reduce potential complications.
Exploring Preeclampsia
What is Preeclampsia?
Preeclampsia is a serious pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and signs of damage to another organ system, most often the liver and kidneys. This condition typically occurs after 20 weeks of gestation and can also develop postpartum. Unlike gestational hypertension, preeclampsia includes additional symptoms such as proteinuria, which is excess protein in the urine indicating kidney damage.
The causes of preeclampsia are not fully understood, but it is believed to result from problems with the placenta. Risk factors include first-time pregnancies, multiple gestations, and pre-existing conditions like chronic hypertension or autoimmune disorders. Without proper management, preeclampsia can lead to serious complications for both mother and baby, including preterm birth and restricted fetal growth.
Early diagnosis and regular monitoring are crucial to managing the condition and minimizing risks. Treatment may involve medication to control blood pressure and, in severe cases, early delivery may be necessary to ensure safety.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Preeclampsia can manifest with a range of symptoms, which may initially be mild but can escalate rapidly. Common warning signs include persistent headaches, vision changes such as blurriness or seeing spots, and swelling in the face, hands, or feet. Sudden weight gain due to fluid retention is another indicator. Some women may experience upper abdominal pain, often under the ribs on the right side, which can indicate liver involvement.

Nausea or vomiting, especially later in pregnancy, can also be a sign. It’s crucial to monitor these symptoms closely, as preeclampsia can progress to severe preeclampsia or eclampsia, leading to potentially life-threatening complications like seizures. Regular prenatal visits enable healthcare providers to detect these symptoms early. Blood pressure checks and urine tests for proteinuria are standard practices for identifying preeclampsia. If you notice any warning signs, contacting a healthcare professional promptly is essential to ensure timely intervention and care.
Potential Complications
Preeclampsia poses significant risks to both mother and baby, making awareness and early intervention crucial. For mothers, severe preeclampsia can lead to complications such as HELLP syndrome—a group of symptoms that affect the blood and liver—and eclampsia, which involves the onset of seizures. Both conditions are medical emergencies requiring immediate attention. Other potential complications include organ damage, particularly to the liver and kidneys, and increased risk of cardiovascular disease later in life.
For the baby, preeclampsia can result in restricted growth due to reduced blood flow to the placenta. This condition can also lead to preterm birth, which carries its own set of health challenges. In severe cases, placental abruption may occur, where the placenta detaches from the uterine wall, posing a life-threatening risk to both mother and baby.
Managing preeclampsia often involves careful monitoring and, in some cases, early delivery to protect the health of both mother and child.
Comparing Hypertension vs Preeclampsia
Key Differences Explained
Understanding the differences between gestational hypertension and preeclampsia is vital for effective pregnancy management. Gestational hypertension is characterized by high blood pressure that develops after the 20th week of pregnancy without other symptoms. In contrast, preeclampsia includes high blood pressure along with additional signs such as proteinuria and organ dysfunction. These differences are crucial, as preeclampsia poses more significant health risks and requires more intensive monitoring and management.
Gestational hypertension can be a precursor to preeclampsia, but not all cases progress. The absence of proteinuria is a distinguishing feature of gestational hypertension, separating it from preeclampsia’s more complex symptomatology. Additionally, preeclampsia can develop postpartum, whereas gestational hypertension resolves after delivery. Recognizing these key differences helps healthcare providers tailor their approach, ensuring appropriate monitoring and intervention.
Early and accurate diagnosis is essential to prevent complications and ensure the safety of both mother and baby throughout the pregnancy journey.
Impact on Pregnancy and Health
Both gestational hypertension and preeclampsia can significantly impact pregnancy and overall health, but the extent and nature of their effects differ. Gestational hypertension primarily affects maternal blood pressure, potentially leading to complications like preterm birth if not managed. However, it usually resolves after delivery and rarely causes long-term health issues if monitored appropriately. In contrast, preeclampsia poses greater risks, affecting multiple organ systems and leading to severe complications like eclampsia or HELLP syndrome.
The condition can also restrict fetal growth due to decreased placental blood flow, increasing the likelihood of preterm delivery. Long-term, women who experience preeclampsia may have an elevated risk of cardiovascular diseases. For the baby, preterm birth can result in various developmental challenges.
Therefore, understanding the impact of these conditions underscores the importance of regular prenatal care and early detection. Effective management strategies can help mitigate these risks, ensuring better health outcomes for both mother and child.
Monitoring and Diagnosis
Effective monitoring and diagnosis are critical in managing gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. Regular prenatal visits are essential, as they allow healthcare providers to track blood pressure levels and detect any early signs of complications. For both conditions, blood pressure readings are a primary diagnostic tool. Gestational hypertension is diagnosed with consistent blood pressure readings of 140/90 mmHg or higher, without additional symptoms.
Conversely, preeclampsia diagnosis involves high blood pressure along with proteinuria or other signs of organ dysfunction. Laboratory tests, such as urine analysis for protein and blood tests to assess liver and kidney function, are vital. Ultrasounds may also be used to monitor fetal growth and placental health. Early detection through these methods enables timely intervention, reducing the risk of severe complications.
Women are encouraged to report any unusual symptoms promptly, ensuring that healthcare providers can adjust their care plan as needed to protect both maternal and fetal health.
Importance of Prenatal Care
Regular Blood Pressure Monitoring
Regular blood pressure monitoring is a cornerstone of prenatal care, crucial for detecting and managing gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. Consistent monitoring helps healthcare providers identify any rise in blood pressure early, allowing for timely intervention. Typically, blood pressure is checked at each prenatal visit, starting from the first trimester through delivery. For expectant mothers, especially those with risk factors, frequent monitoring ensures any changes are promptly addressed, reducing the risk of complications like preterm birth or severe preeclampsia.
Home monitoring can also be beneficial, providing additional data between appointments. Accurate record-keeping of readings can help track trends and inform medical decisions. Regular monitoring is essential for safeguarding maternal and fetal health, enabling healthcare providers to tailor care strategies and interventions as needed. This proactive approach in prenatal care underscores its importance, helping ensure healthier outcomes for both mother and baby throughout the pregnancy journey.
Role of an Obstetrician in Jacksonville, Florida
An obstetrician plays a vital role in prenatal care, particularly in managing conditions like gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. In Jacksonville, Florida, specialists such as those at Trogolo Obstetrics and Gynecology provide comprehensive care tailored to each patient’s needs. Their responsibilities include regular monitoring of blood pressure, conducting necessary tests to detect early signs of complications, and devising management plans to ensure safe pregnancies.
Obstetricians guide expectant mothers through dietary and lifestyle changes that can mitigate risks associated with high blood pressure. They also educate patients about recognizing warning signs and symptoms, empowering them to seek timely medical attention. With their expertise, obstetricians coordinate with other healthcare professionals to provide holistic care, including referrals to specialists if needed.
Their proactive approach and personalized care strategies are crucial for minimizing risks and promoting healthy outcomes for both mothers and their babies, fostering a supportive environment throughout the pregnancy journey.
Support from Trogolo Obstetrics and Gynecology
Trogolo Obstetrics and Gynecology in Jacksonville, Florida, offers comprehensive support for expectant mothers, particularly those at risk for gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. Their team of experienced professionals provides individualized care, ensuring that each patient receives the attention and guidance needed throughout the pregnancy. They emphasize the importance of regular prenatal visits to monitor blood pressure and overall maternal health.
The clinic offers advanced diagnostic tools and tests to detect early signs of hypertension-related complications, facilitating timely interventions. In addition, they provide valuable resources and education, helping patients understand their conditions and empowering them to make informed health decisions. By fostering a supportive and communicative environment, Trogolo Obstetrics and Gynecology ensures that patients have access to the latest information and treatments available.
This comprehensive approach not only enhances maternal and fetal health outcomes but also offers peace of mind to families during this critical time.
Advocating for Your Health
Communicating with Healthcare Providers
Effective communication with healthcare providers is essential for advocating your health during pregnancy, particularly when managing conditions like gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. Clear and open dialogue ensures that healthcare providers fully understand your symptoms, concerns, and medical history. Patients are encouraged to ask questions about their condition, treatment options, and any lifestyle changes that may be beneficial. Keeping a symptom journal, noting any changes or concerns, can be helpful during appointments.
This practice facilitates informed discussions and ensures nothing important is overlooked. Understanding medical advice and following through with recommended tests or treatments is crucial. If anything is unclear, asking for clarification can help prevent misunderstandings. Building a trusting relationship with your healthcare team fosters a collaborative approach to care, enabling better management of your pregnancy. By actively participating in your healthcare decisions, you can help ensure a safer and healthier pregnancy journey for both you and your baby.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Safer Pregnancy
Making informed lifestyle adjustments can significantly enhance safety and health during pregnancy, particularly for those dealing with gestational hypertension or preeclampsia. First, maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help manage blood pressure.
Reducing salt intake is also recommended to minimize fluid retention. Regular, moderate exercise, as advised by a healthcare provider, improves cardiovascular health and overall well-being. Staying hydrated and getting adequate rest are essential for managing stress and promoting health. Avoiding tobacco, alcohol, and illicit substances is crucial, as these can exacerbate pregnancy complications. Stress management techniques, such as prenatal yoga or meditation, may also be beneficial.
Monitoring weight gain and attending regular prenatal appointments help track health progress and address issues early. By taking proactive steps and working with healthcare providers, expectant mothers can create a supportive environment that promotes a safer and healthier pregnancy for themselves and their babies.
Resources and Support Systems
Accessing resources and building support systems are vital for managing health during pregnancy, especially when facing conditions like gestational hypertension or preeclampsia. Numerous resources are available to provide information and assistance, from healthcare professionals to online support groups. Healthcare providers can offer valuable insights into managing these conditions, guiding treatment plans and lifestyle changes.
Additionally, reputable health websites and organizations provide educational materials to help expectant mothers understand their condition better. Support groups, both in-person and online, offer a community of individuals with similar experiences, providing emotional support and practical advice. Family and friends also play a crucial role in offering assistance and encouragement during pregnancy. Engaging with these resources and networks can help alleviate stress and promote a sense of empowerment.
By leveraging available support systems, expectant mothers can navigate the challenges of pregnancy more effectively, enhancing their health and well-being for a safer pregnancy journey. For additional advice, support and help reach out today!