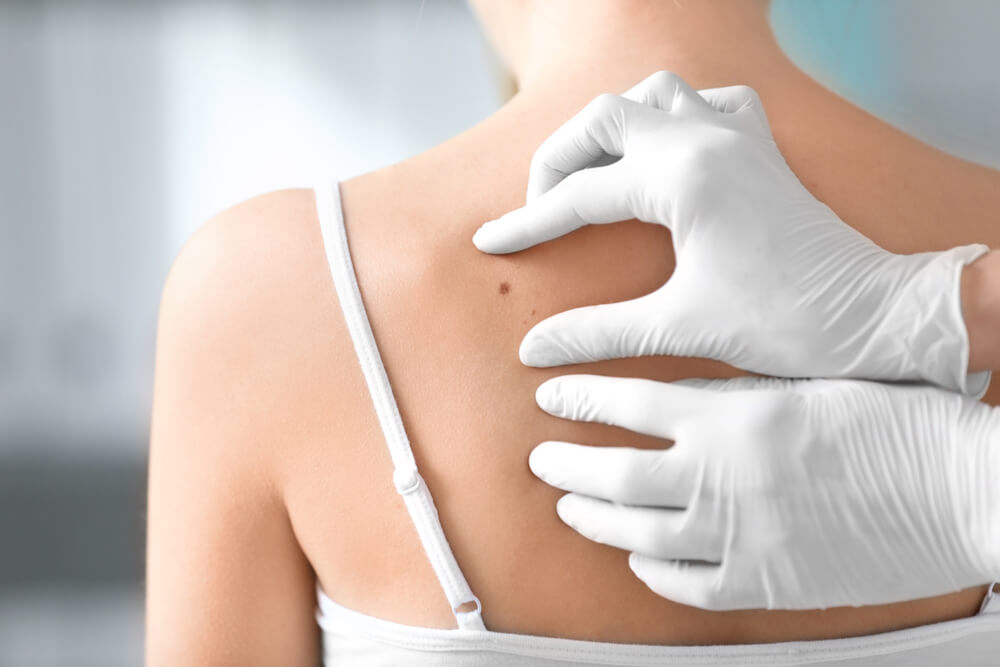
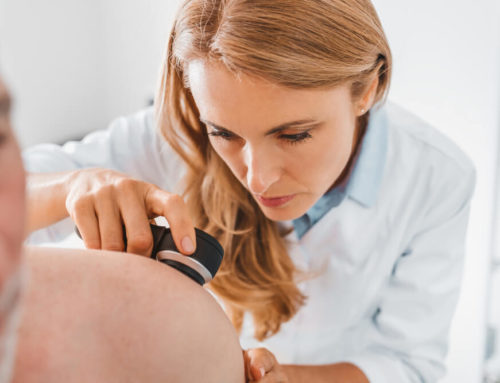
The summer is upon us, and with the beaming sunlight and regular visits to the beach comes potential danger in the form of melanoma – a serious type of skin cancer. But what exactly causes melanoma cancer? And are there different types of melanoma you should be wary of? Also, how fast does melanoma spread, and what are your treatment options? In this expert-approved article on melanoma cancer, you’ll learn about the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment of melanoma cancer.
If you have some previous knowledge of melanoma cancer, you may know that this condition often begins as a mole. In case you need expert guidance, we recommend mole removal in Palm Beach. Always be mindful of any bodily changes, and don’t hesitate to reach out to professionals.
That said, here is everything you ever wanted to know about melanoma cancer.
What is Melanoma Cancer?
Before reading the melanoma cancer symptoms and discussing the different types of melanoma, let’s define what the condition refers to. In the simplest terms, melanoma is the most severe type of skin cancer. It develops in the melanocytes or the cells that produce the pigment that gives skin color, melanin. In some cases, patients may have melanoma in the eyes or even inside the body, including the throat or the nose.
Unfortunately, the exact melanoma cancer cause remains a mystery. However, researchers believe that repeated exposure to UV or ultraviolet radiation from tanning lamps and the sunlight may increase the risk of melanoma cancer. Therefore, one of the best ways to reduce your risk of developing melanoma is by limiting ultraviolet radiation exposure.
Women, especially those under the age of forty, are at high risk of melanoma. Generally, it is believed that younger women spend more time tanning in the sun or in tanning beds without sun protection. Understanding the warning signs of melanoma skin cancer and the risk factors can prevent this condition. Most importantly, detecting and treating melanoma cancer in its early stages prevents it from spreading. When detected early, melanoma is treatable.
Symptoms of Melanoma Cancer
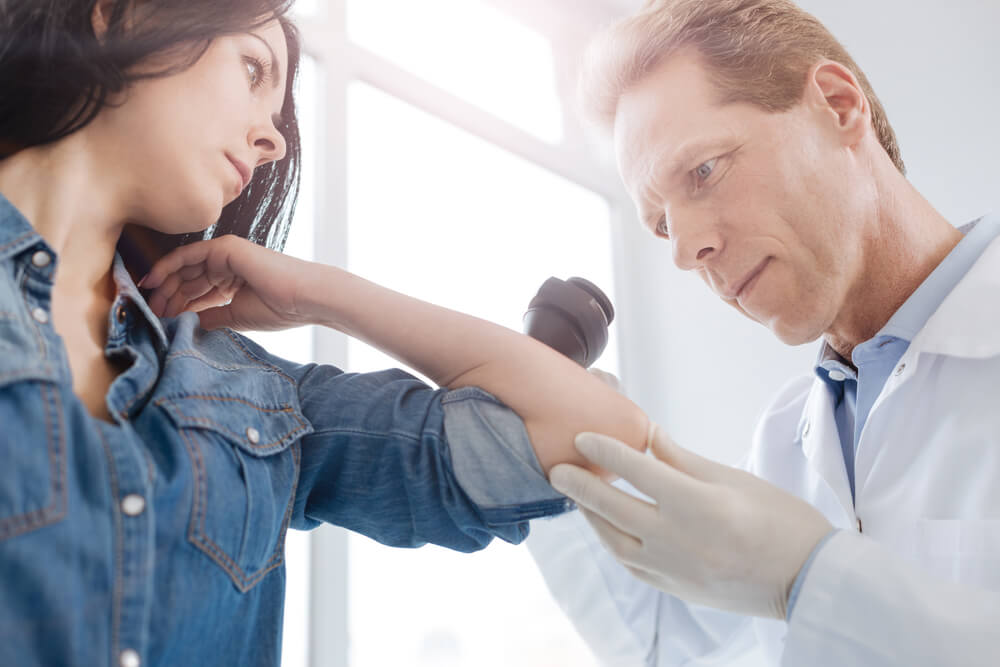
Melanoma cancer may develop anywhere, whether on the arms, face, back, or legs. Typically, melanoma cancer develops in areas exposed to the sun. However, this serious skin cancer can also appear in areas not exposed to the sun, such as fingernail beds, the soles of feet, and the palms. People with darker skin may be at greater risk of these “hidden melanomas.”
The first symptoms and signs of melanoma cancer are a change in an existing mole and the development of an unusual-looking or new pigmented growth on the skin.
Nevertheless, it’s important to remember that melanoma cancer doesn’t always start as a mole. In some instances, patients with “normal” skin may also develop melanoma.
Melanoma Cancer Risk Factors
A few factors may increase your chances of developing melanoma cancer. Here are some of the most common ones to be mindful of.
- Excessive exposure to the sun or tanning beds
- Having a history of sunburn
- Having fair skin
- Living at a higher elevation or closer to the equator
- Having multiple moles, or unusually-looking moles
- Having a family history of melanoma skin cancer
- Having a weak immune system
People with less melanin, or pigment in the skin, have less protection from harmful ultraviolet radiation. For example, if you have fair skin, red or blond hair, light-colored eyes (blue, grey, green), and you sunburn or freckle easily, you are at greater risk of melanoma cancer than people with darker skin. However, melanoma cancer can also develop in patients with darker complexions.
Types of Melanoma
There are four types of melanoma: nodular, acral lentiginous melanoma, superficial spreading, and lentigo maligna.
Nodular melanoma is one of the most common types of melanoma, affecting around fifteen to twenty percent of all melanoma cancers.
This type of melanoma grows into the patient’s skin. Typically, the growth has a mushroom-like shape with a stalk or a stem. Although nodular melanoma is black in most cases, it can also be pink or red. Nodular melanoma may develop on the back, chest, or face.
People with dark complexions (such as those from Hispanic, Asian, and African ancestries) are at greater risk of acral lentiginous melanoma. This type of melanoma isn’t related to sun exposure, and it totals less than five percent of melanoma cases.
Typically, acral lentiginous melanoma appears on the palms, under the nailbed, and on the soles of the feet. Since it’s challenging to see abnormal areas under the nails and on the feet, acral lentiginous melanoma can be difficult to diagnose.
Next is superficial spreading melanoma, the most common one among the different types of melanoma. Approximately seventy percent of all melanomas are superficial spreading ones. Although superficial spreading melanoma grows outward in most cases, it can also spread across your skin’s surface. Unlike some other types of melanoma, superficial spreading ones may also grow down into your skin. Typically, this type of melanoma develops in the legs, arms, and the central area of the body.
Finally, lentigo maligna melanoma often affects older individuals. Around ten to fifteen percent of melanoma cancer cases are lentigo maligna melanoma. Usually, this type of skin cancer starts as a large brown patch. As it grows, the flat patch gets darker in color (it can become black or dark brown).
Diagnosis and Treatment of Melanoma Cancer: What to Expect
To diagnose melanoma cancer, you’ll need to visit your healthcare specialist. First, your doctor will want to perform procedures and tests to diagnose potential skin cancer. These include a physical exam and a biopsy.
During the physical exam, patients may expect a few questions about general health and history of previous conditions. Your doctor may also want to examine your skin to check for melanoma signs. Next up, the doctor will want to remove a tissue sample for testing (a biopsy). The type of procedure will depend on your doctor’s recommendations.
Typically, doctors recommend patients remove all traces of the growth. A popular technique is the “punch biopsy,” a procedure performed with a circular blade. Alternatively, your doctor may perform an excisional biopsy with a scalpel.
FAQ
How Fast Does Melanoma Spread?
Melanoma can grow rapidly. In just six weeks, this disease can be life-threatening. If you leave it untreated, melanoma can spread to other areas of the body. So, don’t wait for the answer to “how fast does melanoma spread?”. Go consult your healthcare professional immediately.
Where Does Melanoma Spread To?
Melanoma can spread from your skin to different areas of your body, including the liver, brain, lymph nodes, lungs, stomach, and bones.
What Does Malignant Melanoma Look Like?
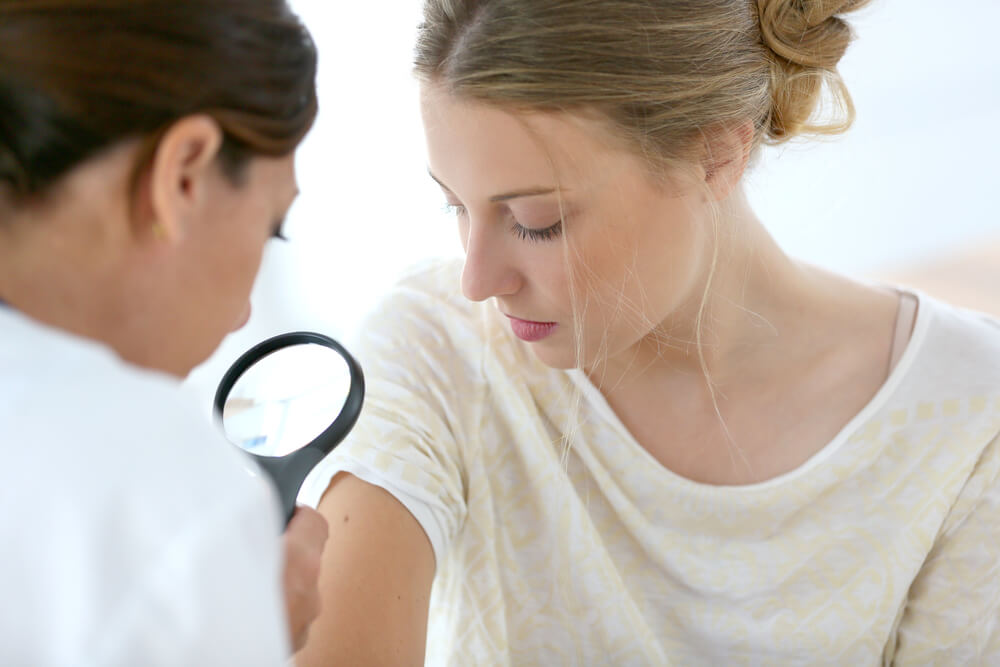

Sometimes, malignant melanoma appears as a rash, sore, bump, or scab that bleeds but doesn’t heal. In other cases, you may see an existing mole become larger and more raised.
Best Prevention Methods
To prevent melanoma:
- Wear sunscreen all year.
- Choose an SPF of at least thirty.
- Wear clothing to shield your skin, such as hats, shirts, and sunglasses.
- Avoid tanning beds and tanning lamps, as they can also increase your cancer risk.
Most importantly, whenever you notice a change in your skin, consult your doctor at once.
Give Us a Call Today
Are you feeling worried and concerned about your health? Book your appointment with us today and let us help you.