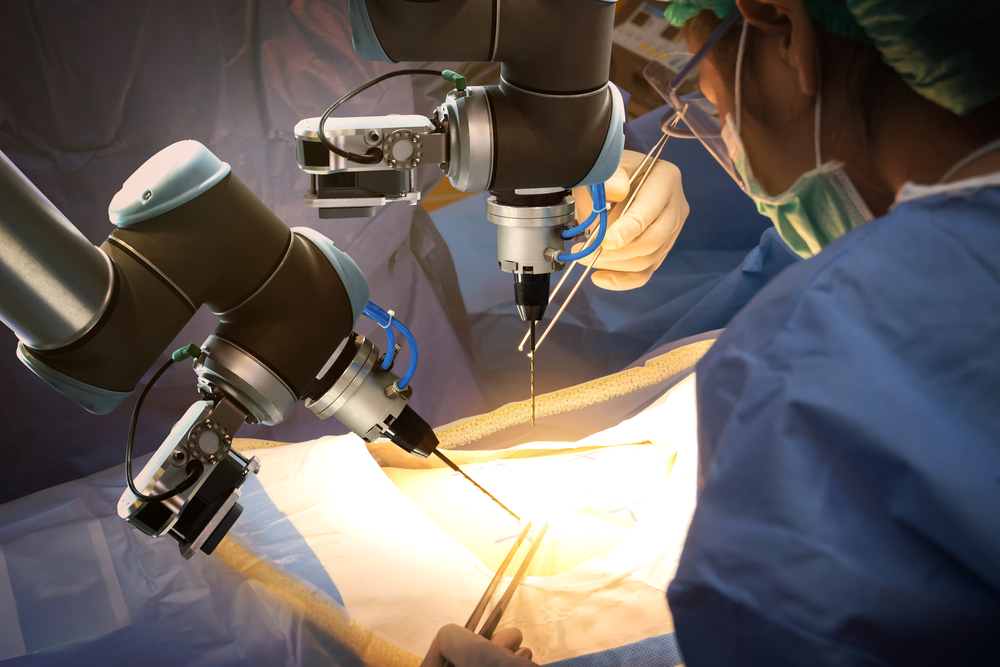
How does robotic surgery work exactly? Is there a difference between regular surgery and surgery involving robotics? Is there a doctor in the house when the machine is turned on and operating? These are just some of the questions people have about robotic surgery. Below is an overview of the topic.
Robotic surgery is a type of surgery performed using the da Vinci robotic surgical system, which has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration. The medical research carried out by Leonardo da Vinci is the inspiration for its name. The system costs about $2 million and uses pre-coded software for its operations, which are directly supervised by a doctor. The point of the da Vinci robotic system is to perform minimally invasive surgery with the ultimate goals of minimal risk of infection and a quicker release from the hospital.
How Does Robotic Surgery Work?
First, the doctor will make small incisions as needed and then insert instruments such as bovies, graspers, scissors or scalpels, and a 3D camera into the incisions. The doctor will sit at a console that’s been compared to a video game because it operates on the same premise: Just as your hand movements control a character on a computer screen, the da Vinci system will respond to the doctor’s movements. The da Vinci robotic system has at least three robotic arms with each one holding a surgical tool or 3D camera. The doctor’s hand movements control the corresponding actions of the robotic arms.
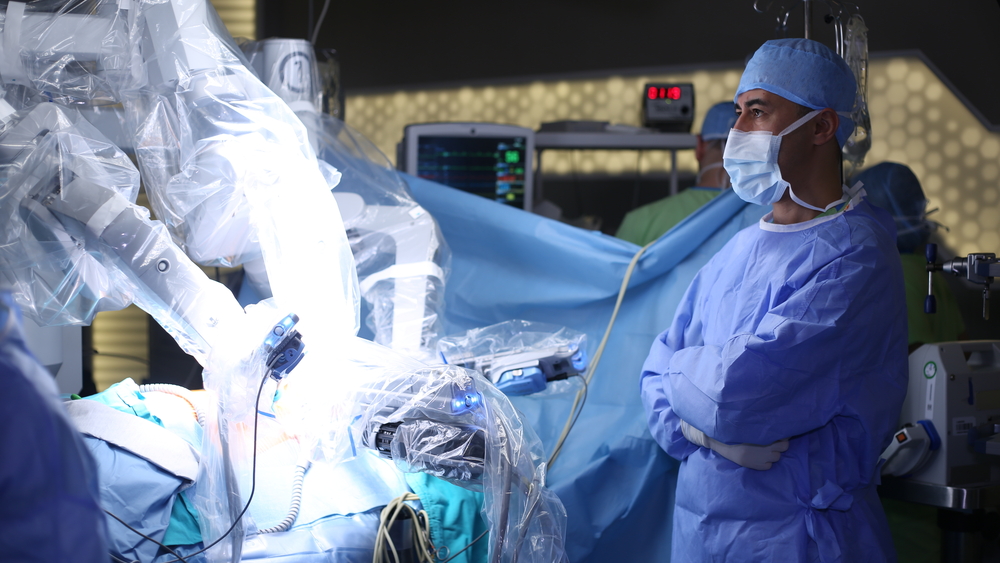
What’s Happening During Robotic Surgery?
It is a straightforward process. The doctor makes the incisions, inserts the tools and camera, and then sits at the computer console to perform the surgery. The 3D camera placed inside the body at the start of the procedure allows the doctor to see images with enhancement and clarity impossible to achieve with the naked eye.
What Are Some More Advantages of Robotic Surgery?
One of the benefits of robotic surgery is that it is only an extension of the doctor’s hand movements. That means that, although the robot is doing the work, the doctor is still in charge.
Another of the advantages of robotic surgery is the more precise movement that a robotic arm can accomplish versus a human’s arm. Each robotic arm has a wider range of motion than a person’s. It can bend and twist in ways that are too stressful or even impossible for a human to perform. In addition to more precision and less human error resulting in blood loss or pain for the patient, this means less fatigue for the doctor.
The system’s high-tech nature gives the doctor the ability to look at surgical areas with higher amplification, which allows for more detailed real-time analysis. Higher amplification through the use of a high-resolution camera means the doctor doesn’t have to sit or stand right next to the patient. Less physical contact should mean less chance of infection.
The goal of robotic surgery in Palm Beach County is more surgical efficiency as well as a speedier, smoother recovery.
What Types of Robotic Surgery Are There?
A variety of procedures are now available through robotic surgery in Palm Beach County. The procedures that the da Vinci system is capable of performing include colorectal, general, gynecologic, heart, endometriosis, head and neck, thoracic, and urologic surgeries. The da Vinci robotic system’s delicate approach allows doctors to access and work on some of the most fragile parts of the human anatomy.
Heart procedures include atrial septal defect and mitral valve repair as well as coronary artery bypass. Thoracic procedures performed may be pulmonary and mediastinal pathologies and complex esophageal surgery. Gastrointestinal surgeries such as bariatric and gastrectomy are also available. Robotic pancreatectomy has resulted in lower estimated blood loss, higher spleen preservation, and shorter hospital stays.
Robotic gynecology can treat conditions of the female internal reproductive system, including the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, and vagina. Treatment is also available for cancer, pelvic organ prolapses, abnormal bleeding, fibroids, endometriosis, and severe pelvic pain.
Robotic treatment of orthopedic issues related to hip and knee problems is a giant leap forward. Surgeons can use computerized tomography (CT) scans to evaluate knee and hip bone size ahead of surgery and make precise calculations regarding how much bone to remove before placing an artificial joint and determining the optimal placement. The robotic system can follow the measurements exactly as directed.
Since 2014, robotic spinal surgery has been an option, and fully robotic kidney transplantation has been available since the late 2000s. Doctors are now using robotics for general surgery as well as for single-quadrant procedures. Robotic urology surgery is now standard. A robotic radical prostatectomy was performed in 2000, and a robot-assisted radical cystectomy has also been performed.
What Kind of Doctors Perform Robotic-Assisted Surgery?
Da Vinci surgical systems are in use worldwide, with some 200,000 surgeries performed in 2012 alone. Currently, nearly 5,000 da Vinci units are in use in the United States, Europe, Asia, and other countries around the globe. It is an advanced system and requires a high level of skill and training to achieve the highest level of care.
How Long Have Robots Assisted in Surgery?
The first robot-assisted surgery was performed in 1985 in Vancouver to help with an orthopedic surgical procedure through voice commands. The robot’s name was Arthrobot. Another robot developed to assist in the operating room was a surgical scrub nurse designed to hand off surgical instruments using voice commands. Also in 1985, a robot called the Unimation PUMA 200 was used to assist in a brain biopsy with CT guidance for a neurological procedure. The Imperial College in London created PROBOT, which performed a prostatic surgery.
An orthopedic robot was built in 1992 to assist in hip replacement surgery. It was the first surgical robot approved by the FDA, with approval in 2008. It coordinated with IBM software to mill out an exact fit for insertion in the femur for hip replacements. That was a considerable advancement over prior hip replacement methods, which entailed a mallet and broach/rasp to carve out a cavity for the artificial joint replacement. The result of that approach was ill-fitting artificial hips that doctors had to make do with by adapting the femur to the metal joint rather than making the joint fit the femur bone as robotic assistance can do now.
These various advancements led to several competing manufacturers of surgical robots. The most prominent were AESOP, followed by ZEUS, and then da Vinci. Eventually, AESOP and ZEUS were merged and combined with da Vinci, which has built on the success of the previous robots.
Robotic-assisted surgery has been around for decades now. It continues to develop, even getting to the point where surgery is now possible by remote control. Doctors have performed long-distance surgery using robotics since 2001, which was the year a remote surgery was performed by a doctor in New York City on a patient in Strasbourg, France.
Robotic-assisted surgery can help alleviate many medical issues and is available at clinics such as Advanced Surgical Physicians. Call to schedule a consultation with one of our doctors who are specially trained in the use of the da Vinci surgical system.