Skin cancer, or abnormal growth of skin cells, most often develops on skin exposed to the sun, but it can also appear on areas of the skin that are generally not exposed to the sun. Skin cancer affects people of all races equally. It is the most common type of cancer in the United States. Current estimates are that approximately 9,500 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with skin cancer every day. Advanced Surgical Physicians’ specialists offer skin cancer treatment in Palm Beach County for many kinds of skin and soft tissue lesions, including benign (non-cancerous) conditions.
Skin Cancer Symptoms
Skin cancer most often develops on the scalp, face, lips, ears, neck, chest, arms, hands, and legs (more often in women). However, it can also develop on areas of the skin that are rarely exposed to sunlight, such as the palms of the hands and the genital region.
Some of the most common symptoms you can experience are:
- a lesion or growth on the skin
- change in the color of the birthmark (brown, black, red, or bluish)
- several different colors on one lesion
- irregular mole edges, usually asymmetrical
- changes in the appearance of the pigmented skin areas over time
- bleeding from a growth on the skin
- new birthmarks, moles, lumps, dark spots
Diagnosis: What Tests Will the Doctor Do?

Different skin cancer types ask for different examination methods. The first step is usually a visit to your GP, who will do the examination and decide if you should be referred to a dermatologist for further tests and treatment. They may also refer you to a surgeon or plastic surgeon. A specialist will know a lot already after a simple examination.
However, it is not always easy to distinguish between skin cancer and benign changes just by examination. They may recommend a biopsy. It is a quick and straightforward procedure that can usually be performed using a local anesthetic. The doctor will remove all or part of the lump and send it to a laboratory for analysis under a microscope. Since basal cell carcinomas rarely spread, no further tests are likely to be needed if the cancer has been completely removed. But since squamous cell carcinomas can sometimes spread, your doctor may want to do a few other tests, a physical exam, and biopsies to ensure there is no need for further treatment. This is especially important if you have already been treated for skin cancer and now it has reappeared.
During the physical exam, the doctor will probably conduct a palpatory examination to see if there are any enlarged lymph glands. X-ray examination, CT, and MRI scans can show metastases. With melanoma, X-rays, CT and MRI scans, and other procedures may also be needed to determine whether the disease has spread (metastasized).
Types of skin cancer
Skin cancer occurs when a mutation occurs in the DNA of skin cells. Mutations cause uncontrolled cell growth and thus, the formation of cancer cells. This form of cancer begins to manifest on the skin’s upper layer, i.e., the epidermis. The area where the cancer appears determines the type and, thus, the treatment options. Much of the DNA damage in skin cells is the result of ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
But please note that sun exposure does not explain skin cancer that occurs on skin that is not otherwise exposed to the sun. This is precisely what proves that other factors can also contribute to an increase in the risk of skin cancer, such as exposure to toxic substances or weakening the immune system.
There are three main types of skin cancer – melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Melanoma
Melanoma is a skin disease in which cancer cells are found in cells that give color to the skin and, therefore, can develop anywhere in the body. The most common symptoms of melanoma are pigmented spots or moles that change color or shape or both and inflammation of the skin that begins to surround an existing mole. It does not always appear on a mole, but it can also appear on normal-looking skin.
Some of the first melanoma symptoms are asymmetrical moles, moles that darken or change color, but also those that grow, bleed, or hurt, pimples that do not heal, especially on parts of the skin that are exposed to the sun, HPV virus, mouth sores that do not heal, dark spots under the nails, and excessive skin peeling.
Basal cell carcinoma
This is a type of cancer of the cells located on the lower part of the uppermost layer of the skin, i.e., the epidermis. It grows slowly and rarely spreads. However, it is crucial to remove it so that the skin ulcer does not appear. It more often occurs after the age of 40 and can be recognized by a spot or lump that is painless but can grow.
Squamous cell carcinoma
This is a type of cancer of the cells of the topmost layer of the skin. It is more aggressive than basal cell cancer, but it can develop slowly. If left untreated, it can spread to other parts of the body. It can also appear on scars, burns, or injuries, and it appears most often in people over 50 years old.
Skin Cancer Treatments
Skin cancer can be successfully treated. Before starting the therapy, the doctor will take into account numerous factors such as age, general health, size and type, and the location of the cancer. The different skin cancer stages will also influence the course of the treatment.
Cancer treatment options vary, depending on the factors listed. In practice, the following methods of treatment are applied:
- Biological therapy – these treatments stimulate the immune system to destroy cancer cells.
- Surgical treatment – surgical treatment involves removing cancer surgically; sometimes, it is necessary to remove the surrounding parts of the skin even though they are not affected by the change. In some cases, it is also necessary to remove nearby lymph nodes. Typically, surgical approaches are the most successful in earlier cancer stages.
- Chemotherapy – involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be taken in tablet form or intravenously/intramuscularly. Chemotherapy is one of the most successful treatment methods because it allows most of the drug to reach growth directly.
- Radiation therapy – involves the use of high doses of X-rays or other high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy is usually an option when the cancer cannot be completely removed during surgery.
Risk Factors
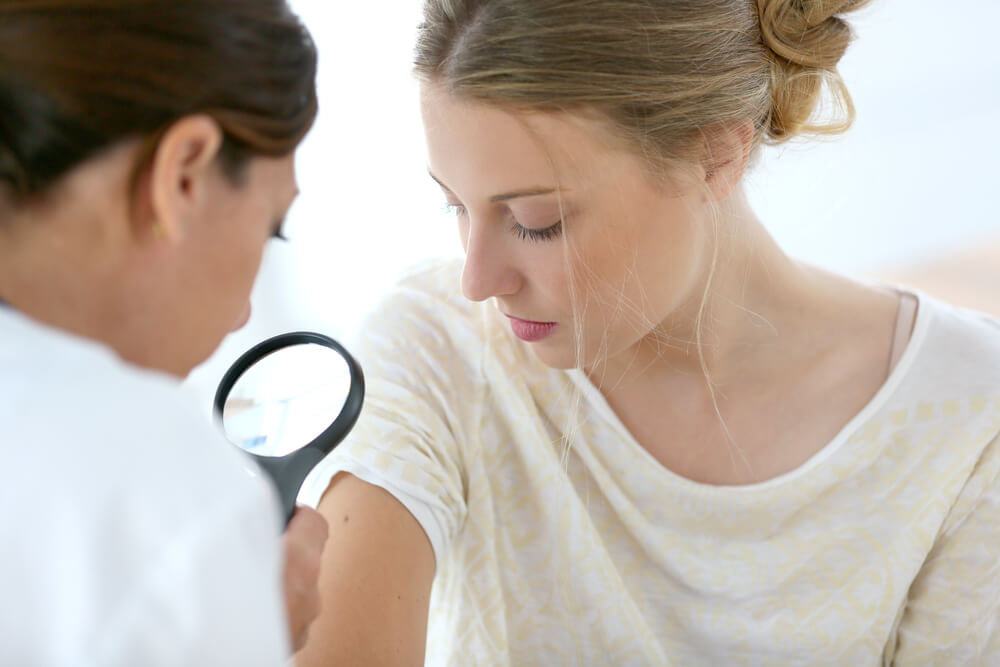

The average risk of developing skin cancer is about 1 in 75, but it can be much higher if you have any of the following risk factors:
- 50 or more birthmarks;
- atypical moles, even just one;
- if you have had a sunburn in the past which resulted in blistered burns;
- sun-sensitive skin that burns easily or freckles form on it;
- you or a family member have had any type of skin cancer;
- use of the solarium.
A simple way to reduce the risk of skin cancer is to follow these rules:
- During the summer months, respect the warnings of experts related to weather conditions (for example, do not go in the sun between 10 AM and 5 PM).
- Check your skin for moles and changes regularly.
- When exposed to sunlight, always use a cream with the highest protection factor (SPF 30 or higher).
- Avoid the solarium!
In 90% of cases, skin cancer is curable if detected early, so contact Advanced Surgical Physicians and schedule your appointment today!