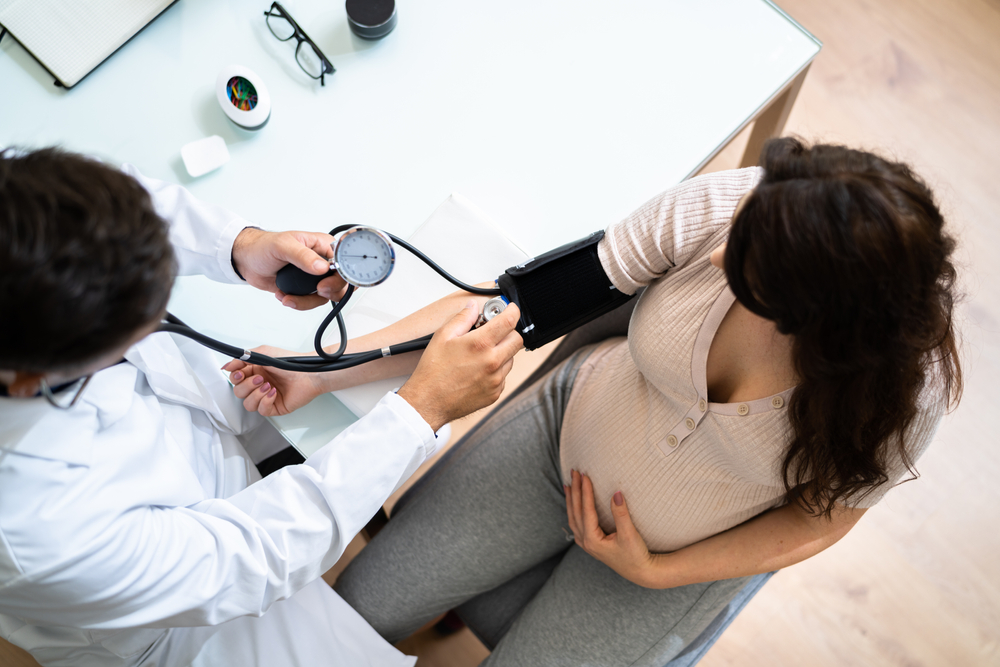
Pregnancy, a miraculous journey, can sometimes be accompanied by unforeseen challenges. One such challenge is gestational hypertension, a condition that merits our attention and understanding. In this blogpost, we talk about the intricacies of high blood pressure in pregnancy, what is gestational hypertension, shedding light on gestational hypertension symptoms, and its underlying causes.
My OBGYN Specialists is one of the most successful medical facilities in the U.S. and it offers its patients premium care and guidance. Choosing a suitable doctor to follow you on your pregnancy journey is one of the most important steps you can make as a future mother, so make sure you do proper research and make the most convenient choice in accordance to your specific needs.
What Is Gestational Hypertension?
Gestational hypertension, a term often heard during prenatal care, refers to high blood pressure that specifically develops after the 20th week of pregnancy. Unlike pre-existing hypertension, gestational hypertension is unique to pregnancy and typically resolves after childbirth. It is characterized by elevated blood pressure readings, often exceeding 140/90 mmHg, without any previous history of high blood pressure.
This condition is a critical concern during pregnancy due to its potential impact on both maternal and fetal health. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and early detection of gestational hypertension are crucial aspects of prenatal care, allowing healthcare providers to intervene promptly and mitigate potential complications.
Understanding the dynamics of gestational hypertension empowers expectant mothers to actively participate in their healthcare journey, fostering a safer and healthier pregnancy experience.
Gestational Hypertension Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of gestational hypertension is essential for early intervention. Here are some of the most common symptoms in patients:
- Elevated Blood Pressure: Gestational hypertension is primarily identified by consistently high blood pressure readings, often exceeding 140/90 mmHg after the 20th week of pregnancy.
- Proteinuria: Presence of excess protein in the urine is a common symptom of gestational hypertension. Regular urine tests during prenatal check-ups help detect proteinuria.
- Swelling (Edema): Swelling, especially in the hands and face, is a noticeable symptom. While mild swelling is common in pregnancy, sudden or severe edema may be indicative of gestational hypertension.
- Headaches: Persistent headaches, especially those not typically experienced before pregnancy, may be a symptom of gestational hypertension. Monitoring the frequency and intensity of headaches is crucial.
- Visual Disturbances: Some women with gestational hypertension may experience visual disturbances such as blurred vision, spots, or light sensitivity. These symptoms warrant immediate medical attention.
- Abdominal Pain: Abdominal pain, often in the upper right side, can be a sign of complications related to gestational hypertension. It may indicate issues with the liver or other organs.
- Nausea or Vomiting: While common in pregnancy, persistent nausea or vomiting, especially accompanied by other symptoms, may be indicative of gestational hypertension and should be reported to healthcare providers.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or increased shortness of breath can be associated with gestational hypertension, particularly if it is accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
- Reduced Fetal Movement: Changes in fetal movement patterns, such as a decrease in activity, may signal potential complications related to gestational hypertension. Regular fetal monitoring is essential.
- Weight Gain: Rapid or excessive weight gain, especially in the second half of pregnancy, can be a symptom of gestational hypertension. Monitoring weight gain and reporting sudden increases is crucial for early intervention.
It is essential to note that these symptoms can vary in intensity and may not be exclusive to gestational hypertension. Any concerns or unusual symptoms during pregnancy should be promptly discussed with healthcare providers for a thorough evaluation and appropriate guidance.
Regular prenatal check-ups play a vital role in monitoring and addressing these symptoms to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
What Causes Gestational Hypertension?
The precise causes of gestational hypertension remain elusive, but several factors contribute to its development. Understanding these factors is key to preventing and managing this condition effectively:
- Placental Issues: One leading cause of gestational hypertension lies in placental problems. Insufficient blood flow to the placenta can trigger an increase in blood pressure. Regular monitoring of the placenta’s health is crucial to identifying and addressing potential complications.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy induces various hormonal changes, some of which can impact blood pressure regulation. Fluctuations in hormones like progesterone may contribute to elevated blood pressure levels during gestation.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Women with pre-existing conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, or autoimmune disorders are at a higher risk of developing gestational hypertension. Managing these conditions before and during pregnancy is vital in preventing complications.
- First-time Pregnancy: First-time pregnancies carry a higher risk of gestational hypertension. The body’s response to the unique challenges of pregnancy may differ in first pregnancies, potentially leading to elevated blood pressure.
- Age and Obesity: Advanced maternal age and obesity are additional risk factors for gestational hypertension. These factors may exacerbate the strain on the cardiovascular system, increasing the likelihood of developing high blood pressure during pregnancy.
Managing Gestational Hypertension
Managing gestational hypertension is a collaborative effort between the expectant mother and her healthcare team to ensure a safe pregnancy journey. Regular prenatal check-ups are paramount for monitoring blood pressure levels, allowing healthcare providers to detect any deviations promptly. Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing gestational hypertension.
These may include adopting a balanced and low-sodium diet, engaging in regular, moderate exercise as advised by healthcare professionals, and maintaining a healthy weight. Adequate rest and stress management are also essential components of a comprehensive strategy to control blood pressure during pregnancy.
In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend medication to manage gestational hypertension, emphasizing the importance of adherence to prescribed treatments while closely monitoring potential side effects.
Close communication with healthcare providers is key throughout the pregnancy. Expectant mothers should report any concerning symptoms promptly, such as persistent headaches, visual disturbances, or sudden swelling. Monitoring fetal well-being through regular ultrasound examinations and fetal heart rate monitoring provides additional insights into the impact of gestational hypertension on the baby.
With proactive management, timely interventions, and a collaborative approach between the mother and healthcare team, the adverse effects of gestational hypertension can be minimized, contributing to a healthier outcome for both mother and baby. Managing gestational hypertension requires a holistic approach that prioritizes both the immediate health of the mother and the long-term well-being of the developing fetus.
Conclusion
Gestational hypertension, though a complex condition, can be navigated with knowledge and proactive healthcare. Expectant mothers must be aware of the potential risks, symptoms, and causes associated with high blood pressure during pregnancy. By understanding gestational hypertension, women can take charge of their health, ensuring a safer and healthier journey into motherhood.
Regular prenatal care, coupled with lifestyle modifications, empowers mothers to navigate this challenge with resilience and confidence. For support in this process, and all other potential issues our team is here. Feel free to contact us and ask away! Your health is our number one priority.