Pregnancy is one of life’s most cherished moments. For some, it’s a long-awaited dream or the end of a long and bittersweet journey. For others, it’s a familiar moment. No matter the situation, the last thing a newly pregnant woman wants to think about is what could go wrong. Yet, ectopic pregnancies affect nearly 1 in 100 women.
The best way to dispel anxieties about an ectopic pregnancy is to understand it better. Knowing how an ectopic pregnancy occurs, the treatment options available, and the possible outcomes can help prepare you for an ectopic pregnancy.
At South Miami OG-GYN Associates, we aim to empower you with the knowledge to make the best decisions for your body. If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, schedule an appointment with the best OB-GYN clinic in South Miami and Downtown Doral.
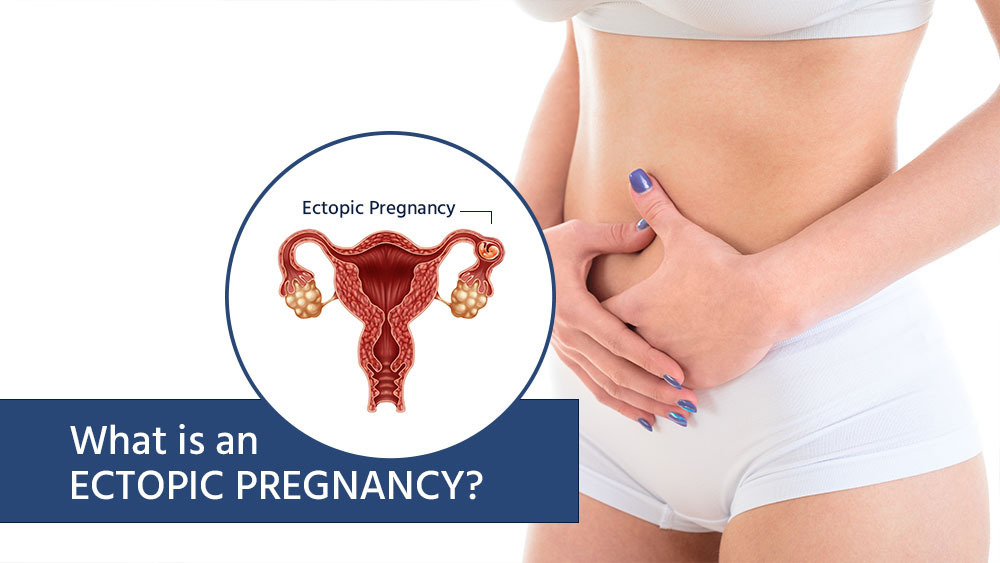
What Is an Ectopic Pregnancy?

When a fertilized egg begins growing outside of the uterus, this is called an ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancies, which usually occur in the fallopian tube (also referred to as a “tubal pregnancy”), can be dangerous for the mom because a fallopian tube isn’t designed to support a growing egg. If left untreated, the tube can rupture, causing life-threatening internal bleeding. According to Hopkins Medicine, untreated ectopic pregnancies are the leading cause of death among pregnant women in the first three months of their pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancies can also occur in other areas of the body outside of the uterus, such as the ovary (called an ovarian pregnancy), abdominal cavity, and cervix. Unfortunately, a fertilized egg cannot survive and grow if it implants outside of the uterus Therefore, pregnancies that become ectopic are not viable.
How an ectopic and ovarian pregnancy is diagnosed:
- A blood test: When you are pregnant, your body produces human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone that can be detected in your urine and blood. The blood test is more accurate than the urine test and can detect the exact amount of hCG in your blood. Your hCG levels can be an indicator of an ectopic pregnancy. High levels indicate a healthy uterine pregnancy; low levels can be an indicator of an ectopic pregnancy, incorrect due date, a blighted ovum, or a possible miscarriage.
- An ultrasound exam: An ultrasound is used to identify where the fertilized egg has implanted using sound waves to create an internal picture.
-
What are the Signs of an Ectopic Pregnancy?
Some women are asymptomatic. They simply miss their period or have a positive pregnancy test.
For many, the first warning sign of an ectopic pregnancy is vaginal bleeding and/or pelvic pain. Vaginal bleeding can resemble your normal period though the consistency and color are often different. Keep in mind that vaginal bleeding is relatively common during pregnancy and does not necessarily indicate an ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage.
Other symptoms may include:
- Lower abdominal pain, often on one side
- Nausea and diarrhea
- Feeling weak or dizzy
While some of these symptoms may be unrelated to an ectopic pregnancy, it is prudent to call your OB-GYN immediately.
Who Is Most At-Risk for Having an Ectopic Pregnancy?
While an ovarian pregnancy or other forms of ectopic pregnancy can affect any woman, some specific circumstances may make some women more susceptible than others.
Ectopic pregnancies occur more commonly among women who:
- Smoke
- Have endometriosis
- Are older in age (35-40)
- Have had an ectopic pregnancy before
- Have had a previous tubal surgery
- Have an IUD or have had their “tubes tied”
- Have had a sexually transmitted disease that caused pelvic inflammatory disease
- Have had trouble conceiving
- Have undergone fertility treatment
There is no way to completely prevent an ectopic pregnancy, but adjusting your health and lifestyle habits can decrease your risk.
What are the Treatment Options for an Ectopic Pregnancy?

An ectopic pregnancy does not resolve on its own, so treatment is always required.
Non-Surgical Treatment:
Methotrexate Injection: An early ectopic pregnancy may be treated with a methotrexate injection. This injection is less invasive than a laparotomy and is generally effective in stopping the growth of the fertilized egg within the fallopian tube.
In most cases, a single injection treats the egg and allows your body to absorb the pregnancy. But some women require a second injection. In either case, your doctor will have you come back for follow-ups to check your hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) levels.
Surgical Treatment:
Laparoscopy/Laparotomy: The symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy typically begin six to eight weeks after the last normal period. If any irregular vaginal bleeding or pain in the abdominal area occurs at this time, it’s important to contact your OB-GYN immediately. This could possibly indicate a ruptured fallopian tube, requiring a laparoscopy/laparotomy.
A laparoscopy is small surgical incisions made into the abdominal cavity. If the fallopian tube has ruptured or is at high risk for rupturing, your doctor will prescribe an emergency laparoscopy. During the procedure, you will be under anesthesia. The decision to perform a laparoscopy/laparotomy will depend on the specific circumstances of the individual case.
Salpingectomy: A salpingectomy may be required if an ectopic pregnancy has caused one of the fallopian tubes to rupture. A salpingectomy is a surgical procedure that is performed to remove the affected fallopian tubes.
The length of a salpingectomy procedure can vary depending on several factors, such as the surgical approach used. In general, however, the procedure takes anywhere from 30 minutes to a couple of hours. After the procedure, your doctor will make several post-treatment care recommendations.
Recovering from a salpingectomy may include:
- Pain management prescription
- A hospital stay (though the procedure is usually outpatient)
- Follow-up appointments to monitor recovery
- Detailed instructions for at-home incision care
- Restrictions on physical activities, such as heavy lifting and sex
Visit the Best OB-GYN Clinic in South Miami and Downtown Doral
The obstetricians at South Miami OB-GYN have helped dozens of women with their unique pregnancy journeys. From prenatal care, screenings, and management of high-risk pregnancies to complicated deliveries, our experts are here to help you every step of the way.
Schedule your visit at the best OB-GYN clinic in South Miami and Downtown Doral online or call 305.665.1133.